One of the best ways to learn what works and what doesn’t work when it comes to UI and usability is to look at as many samples as possible and test out pages, comparing and evaluating how certain elements are being treated.
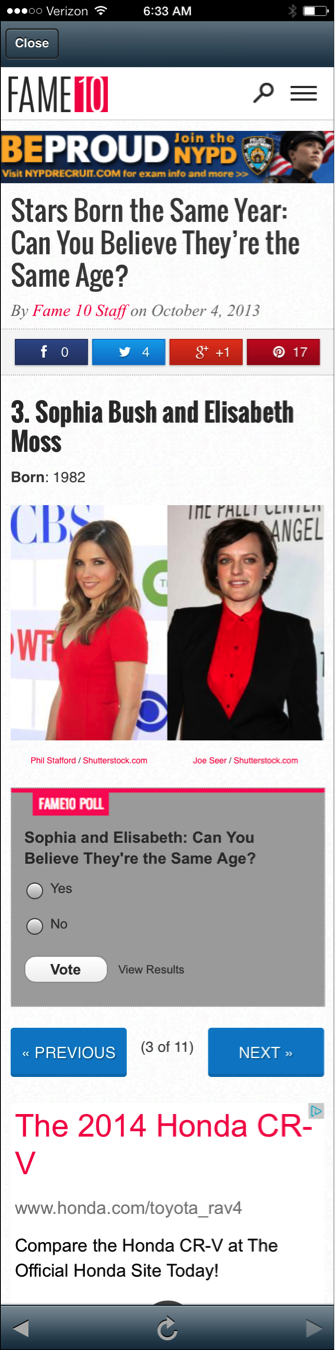
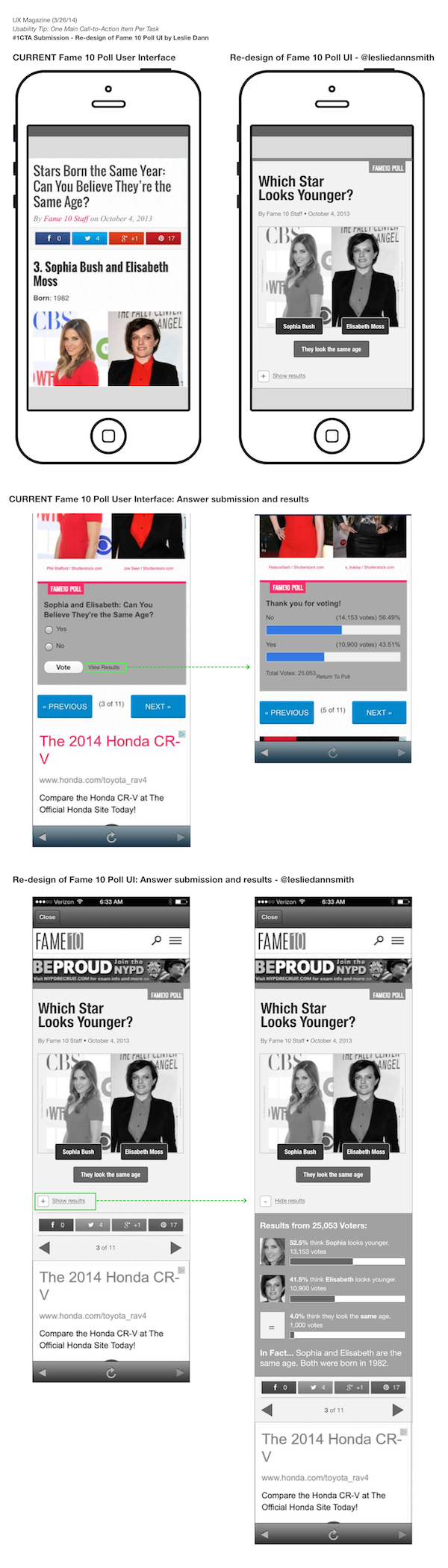
This online poll from Fame10 was linked to through the Fox News mobile app. In the survey, users are asked to submit their answers through radio button selections.
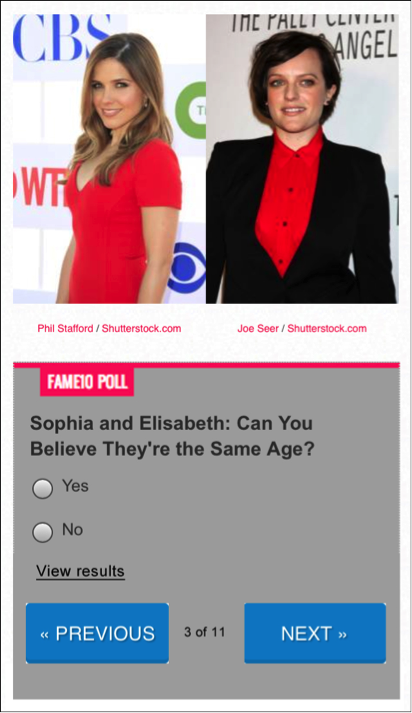
The point is to go through the entire set of questions and vote on each. The problem is, there isn’t a clear call to action that handles both the submission of each response and moving forward to the next set of questions. Instead, users must take two actions, first Vote and then click Next in order to advance forward. To make matters more confusing, the Vote button leads users to the View Results screen (same screen users land on when clicking View Results link).
Cut Through Confusion
As a rule of thumb, the main call to action on a page should be heaviest in weight when compared to other buttons and/or links. All other action items should appear secondary in terms of color, placement, shape, and overall weight allocation. In this case, it seems there are two main call-to-actions which are both required in order to move forward.
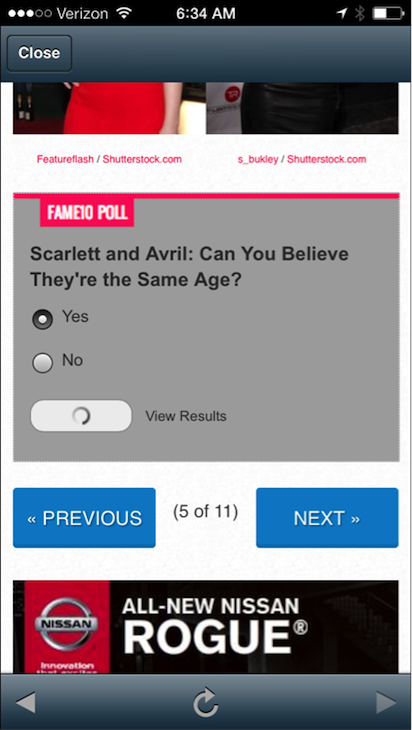
- The NEXT button is the one that stands out most. Its large size and bright blue color comes forward in the design, its letters are all capitalized, and it has a forward arrow icon on it.
- The Vote button appears secondary, as it’s smaller. However, its placement inside the voting gray box indicates it is the main call to action for users who want to vote.
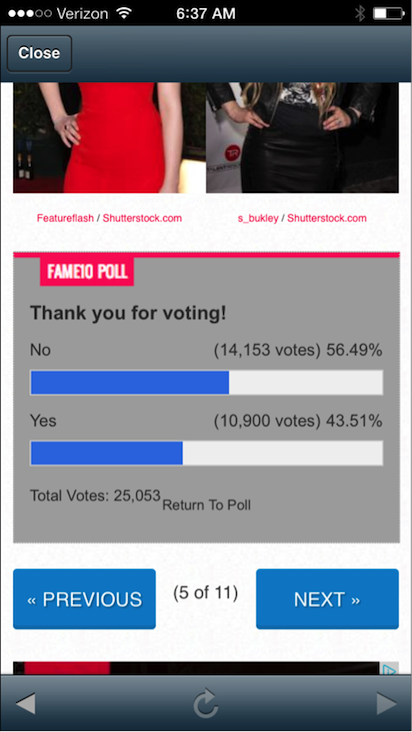
- The View Results link is well designed as a tertiary level call-to-action and presented as a text link versus a button. The confusing part is that it leads to the same results screen that users see after placing their vote which means that users get to see the general poll results whether asking for it or not.
Selection of radio buttons and select Vote. Note: the form is being submitted but the page did not advance to the next set of questions.
Results screen after selecting the Vote button.
Easy Fix
Reduce the number of main call-to-action buttons and allow users to submit and advance to the next screen with one click. Further, only display poll results when users ask for it, via the results link. This will allow a faster form completion, which will most likely lead to more questions being answered by users.
Share your redesign solutions to this problem on Twitter, Facebook, or Google+ using the hashtag #1CTA. We’ll add our favorite submissions to this article abelow. (Image of finger in the air courtesy Shutterstock)