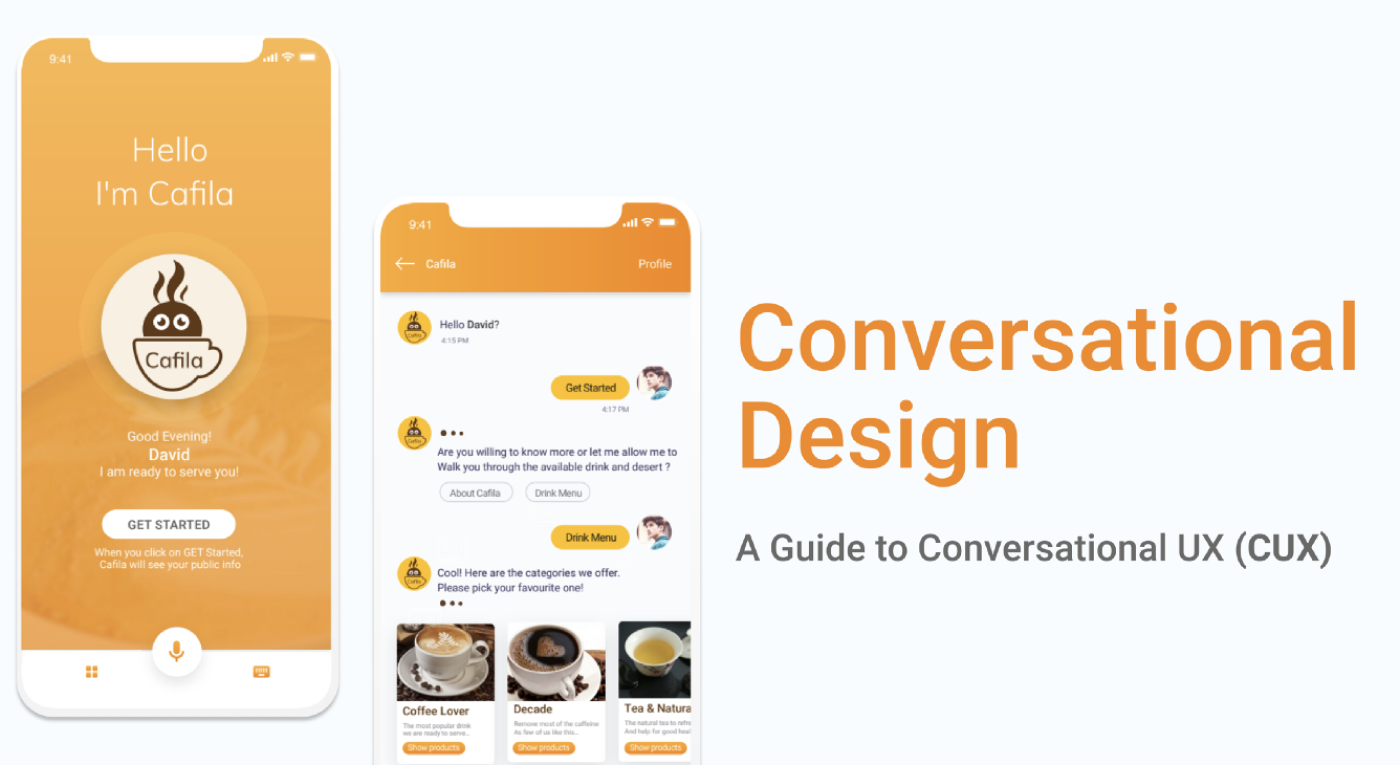
Conversation Design (part of Conversational AI) is all about creating an experience on how human interacts with the system with limited discoverability.
Conversational UX is a user experience that combines chat, voice or any other natural language-based technology to mimic a human conversation. It is a process, where we can define the functional design of UX in a domain that does not require traditional User Interface.
The Three pillars of Conversational UX
- Navigation — Navigate through complex Conversational Flow
- Discoverability — Find out what’s possible and what is not
- Usability — Achieve User goals
Key differences from traditional UX
- Design mockups communicate conversation flow rather than visual design
- Show brand without logos, colours or style guide
- Craft copy in small but very important chunks (micro copy)
Conversational UX Design Methodology (The Design process)

- Do user research and competitive analysis to understand your user and business goal
- Build Personas for Users as well as your bot or virtual assistant (it doesn’t seem like a robot)
- From the user’s stories build the conversational flow.
Structure of conversation (Information Architecture)
Guide the user from start to end through the user stories. It is a back-and-forth journey.
- Write a professional script (Microcopy). sometimes using slang, so you need to include different types of words that the bot will use to recognize the intent.
- Create the Layout, Interaction, visuals, and motions. A detailed design of the dialog with visual elements. Add visual and textual clues and hints — If a user feels lost, guide them through other mediums (other than voice). This way, you will improve the discoverability of your service.
- Simulate your conversational flow (Play the prototype) and walk through with stakeholder
- Continuous testing to evaluate the conversations (user input & bot response)
Before dip drive into the process, here are a few UX principles that play a vital role in conversion design.
Conversational UX Principles
Affordances
Affordances suggest how to interact with an object (here with a bot / virtual assistant). A good design should make the affordances of the product visible and obvious. In a bot scenario — what is the purpose and how to interact with it.
- A text box suggests that I can say and type my intention.
- A send button suggests that the text I type will be sent to the bot.
- Other visual elements like quick replies, cards, carousels, and buttons should be visible!
Many new users don’t figure out how to interact with a device with minimal visual cue. So, help new users understand what these are.
Now about hidden affordances.
For example, the user wants to reset the conversation but is not able to find the reset icon (hidden inside the three dots or ham-burger menu.) Making affordances perceivable can help.
Signifiers
Signifiers can be used to help users identify and use affordances appropriately ( a signal to use affordance).
Quick onboarding sessions showing them the interactional devices, affordances, and how they should be used, can help.
A few buttons appearing initially in the conversation can have labels starting with action words like ‘press’ or ‘click’ (e.g. ‘press for x’s, ‘press for y’, etc) to make it obvious that the buttons (however much they don’t look like standard buttons) are pressable.
Another place where signifiers can be used is to let the user know what the next appropriate action is — should the user consider pressing buttons to respond or type in some text. Perhaps the placeholder text in the text input field could be used to let the user know.
Feedback
Feedback refers to the signal that a product provides its user when it is carrying out an operation that the user requested it to do. Send acknowledgements (e.g. ‘Okay, you want to transfer $200 to the account end with 0345.’) to indicate that the request has been understood.
Below are the elements which keep engaging the user by sending feedback, and set the right expectation, and not leaving the user wondering what’s going on.
Acknowledgment
Ensures user that their input has been received.
Example: Okay. — you want to transfer $200 to the account that ended with 0345.
Confirmation
Provide confirmation on how the bot understood user input
Example: Okay. — you want to transfer $200 to the account that ended with 0345. Would you like to make any changes or allow me to transfer the money?
Error
Errors happen when the bot doesn’t understand the user input/request or the user input is wrong.
Example: Sorry, it seems you have less balance in your present account.
Ending
There should be a natural end to the conversation.
Example: Your amount has been transferred. Is there anything I can help you with? Have a good day!
Feedback also lets users take corrective or affirmative actions.
Affirmative — When the Bot does understand the user phrase, it should respond with an affirmative message that confirms the same.
For example: instead of saying “Okay”, The bot should say — Okay. — you want to transfer $200 to the account that ended with 0345. Are you sure you would like me to transfer the money?
Corrective — When the Bot is unable to understand the user phrase, it should respond with a corrective option or provide suggestions. This allows the user to select another option or restart the conversation entirely.
EXAMPLE-
Let’s consider a Coffee store that wants to build a virtual assistant to enhance its business operations and customer services
1. Set user and business goals.
The user goals
Directly chat with the virtual agent with zero time waiting
- To book a table
- Order online
- Know about the location
- Any customer support
Business goals
- Better user engagement
- Enhance in-store experience
- Quick customer service support
2. Personas
User Persona
A user persona is a semi-fictional representation of a specific segment of your target audience who the users are and their basic needs and requirements and in creating dialogue Few key elements of a user persona are demographics, Psychology (goal, motivations).
The user is David — a busy tech professional who stays alone generally ordering online while driving.
What is a Bot Persona
A bot persona is a character behind the bot. Like user personas, it has a personality and identity.
It’s there to give your customers a consistent experience that doesn’t feel like a monotonous conversation with a robot.
This character represents your brand, hence it has manners, knowledge, and the attitude of a human agent.
Cafila is a Bot — a virtual assistant that helps customers with ordering, FAQ, and order tracking with zero waiting time.
3. Build the User stories
Once the user and bot personas are decided, it is time to write the user stories, which convey the user’s needs and what they want to accomplish when engaging with the bot.
For example – for a coffee Bot- the user stories may be
Find the location near me
Show Menus
Order online or book a table.
Outline the dialogue flow
A Skeleton or sample dialogues between Bot and User. Designers work on a conversation design canvas to build a natural conversation flow. The flow may be linear or no-linear
A linear conversational flow is a question-answer model which doesn’t give any options to move away from the main subject of the conversation.
A non-linear conversation flow allows for conversation to take various routes during the conversation including moving backward or stirring towards another topic.
Information Architecture helps to Set the complete conversational flow
Navigation + Discoverability
Local Navigation
Change the topic of the conversation
Let’s say Location or order online, the bot will show the same
Global Navigation
Global keywords that change the context.
Like, say order online any time in the conversation to go to order.
Way finding
Using words like menu will go to the main menu.
4. Start Writing Your copy (Finally)
Once the flow diagram is in place, Now it is time to focus on copy.
Focus on the personality, your linguist skill, and visual elements
Personality
Set the tone (casual or formal)
Contractions don’t or do not
Emoji — Inside the prompt or replies
Writing copy
Follow all the principles of writing principles, grammar (tense, part of speech, singular or plural)
Be more human (No Robotic)
Finalize visual assets
Use the visual assets to complete the layout design
Conversational User Interface & Principles
It consists of Layout, Interaction, visuals, and motions. A detailed design of the dialog with visual elements.
Frequently used UI controls are
Text, Buttons, cards, Carrousel, Media
Below are the Conversational User Interface Principles
1. Cooperative Principle (Discover hidden intentions)
The cooperative principle was first phrased by philosopher Paul Grice in 1975 as part of his pragmatic theory. According to this principle, An interactive system needs to be cooperative and able to provide the right information with little effort from the user.
The conversation should be relevant, informative, polite in manner, and extract the hidden context
User — “Do you know the actor in this movie?”
Bot: “Yes.”
It’s completely grammatically correct. Yet, it’s weird. Though the user asks a yes/no question the expectation is the Name of the actor.
Below are a few key elements of the cooperative principle
- Quantity: Say as much information as is needed and no more, while being as informative as possible. (Answer only what has been asked)
- Quality: Speak the truth and to the point only.
- Relevance: Talk about what is relevant to the conversation at hand. Irrelevant responses should be avoided.
- Manner: Orderly response and avoid doubts. Try to be clear and explain in a way that makes sense to others.
2. Turn-Taking (give users a space to interact)
The conversation is the art of listening and responding, the objective is to engage users by letting them actively participate in a conversation.
To avoid feeling one-sided, functional conversations should avoid long monologues on the part of the system and make it clear whose turn it is at every moment.
Just as a good storyteller can keep an audience engaged for a long time without being rude, responding to contextual cues and requesting or providing the right information at the right time helps system interactions feel more intuitive.
Be concise! Concise!! Concise!!!
Break up longer messages by providing Chips and buttons (Vertically)
Use carousels to display information with CTA (Horizontally)
- Offer three options only for each conversation item.
- If more options are mandatory, group them into a fourth act of “more options”.
- The “Help” option should be mandatory
- Avoid abbreviations in language.
Ask questions,
Ask closed-ended questions as possible
Use buttons to make replies easy
Example –
Which one of these locations would you like to book a reservation for?
Be clear with open-ended questions
Give an example of what you expect
Type of reply and its format.
Example –
What is your Zip code or which location are you from?
Show the hint (94086)
3. Context-aware (in context / Out of Context)
Humans are unpredictable. We may switch to another topic anytime in between a conversation. The NLP model helps the bot to anticipate what users want and expect during each stage of the communication process and help respond appropriately.
Design to learn, remember
Like we humans, remember and learn from conversations, Bot should learn/ remember when the user tells something.
Example
The user wants to transfer $200 from his account to his friend’s account today at 10 am and suddenly asks a question to Bot about the gold price today. In this scenario, Bot should answer the gold price first (where remember the Amount, account details, and when to transfer to continue the flow.)
Challenges
While designing virtual assistants — two things are taken into consideration
- How to set user expectations and educate users about what their assistants can do
- How to help these users while they are learning or even afterward as the assistant adds new skills.
Final Thoughts
A Conversational UX is all about good storytelling,
where Context is the King and content is the Queen.