Introduction
The Gartner Chatbot Deployment Guide provides practical insight into the state of play of chatbot implementations. And what measures can be taken to improve the chances of success of an implementation.
10 key takeaways from the report:
1.Chatbot teams must focus more on customer intent, rather than technology features and metrics like containment.
2. A lack of focus on intents leads to poor user experience. Customer conversations and utterances do exist from current customer care interfaces like IVR, email, etc. These utterances/conversations can be used for creating intent clusters that are semantically similar.
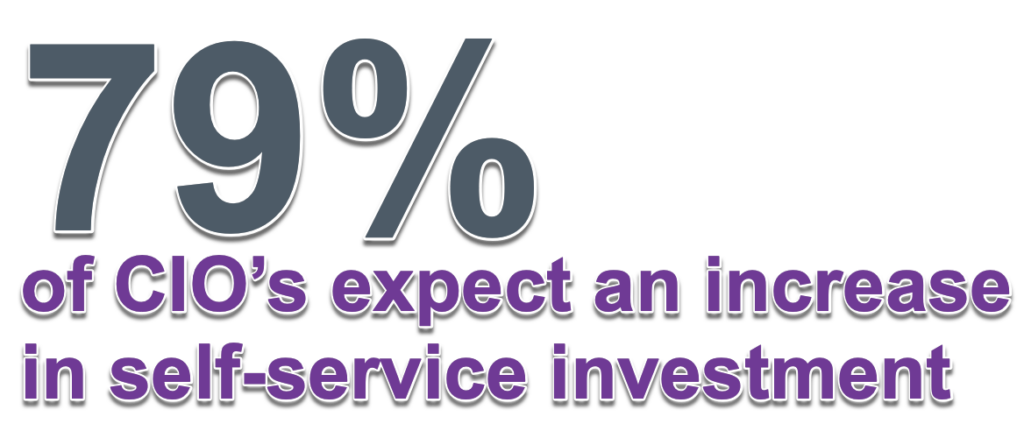
3. When designing a chatbot, companies mistakenly focus on selecting the right technology with attention on feature matrixes and comparisons, instead of focussing on the use-cases and which use-cases to cover. When the intent based use-cases are defined, the technology choices will be much easier.
4. Due to use-cases not being clearly defined, the dependancies of the use-cases are neglected, and this in turn leads to delays.
5. The use-case selection is also important in the sense that it determines the complexity of the implementation project. Failure to define the use-case leads to bad planning and budget complications.
6. According to Gartner, chatbot deployment costs can range from $50,000 to a few million U.S. dollars, depending on the use-case and the technology stack applied.
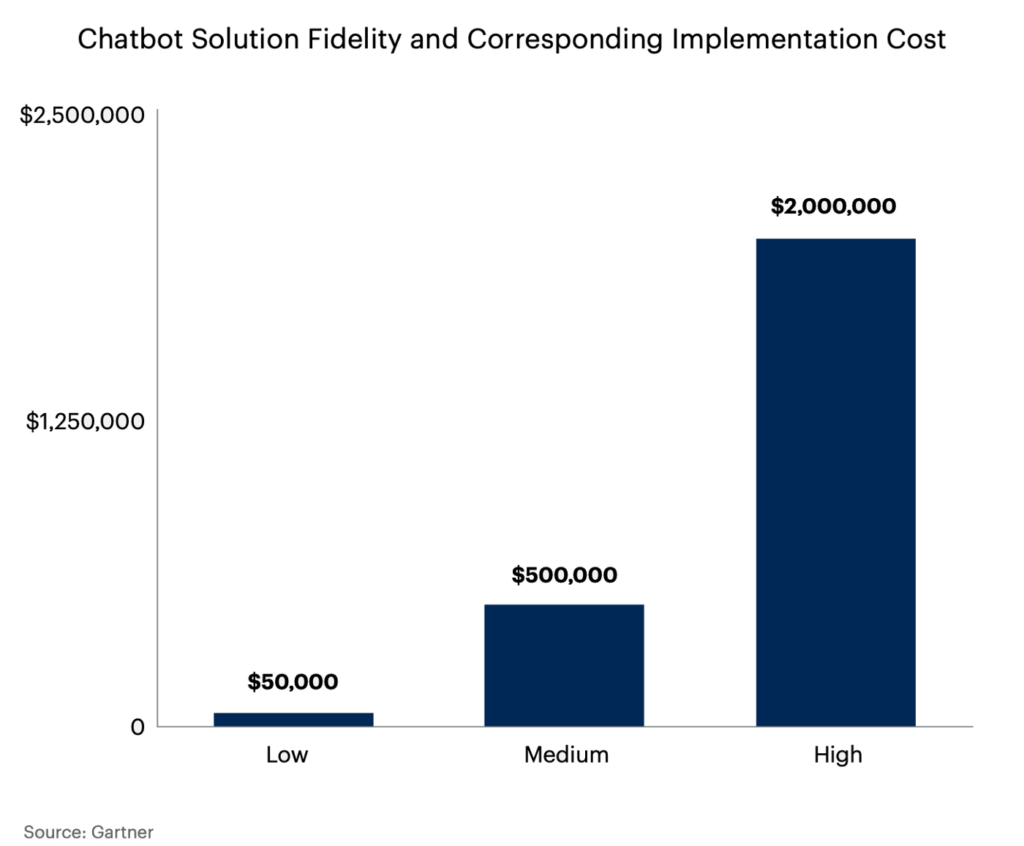
7. The use-case will also determine if the implementation is a low, medium or high fidelity solution.
8. AI must be used in conjunction with chatbot technologies to solve for customer intent in order to achieve business goals.
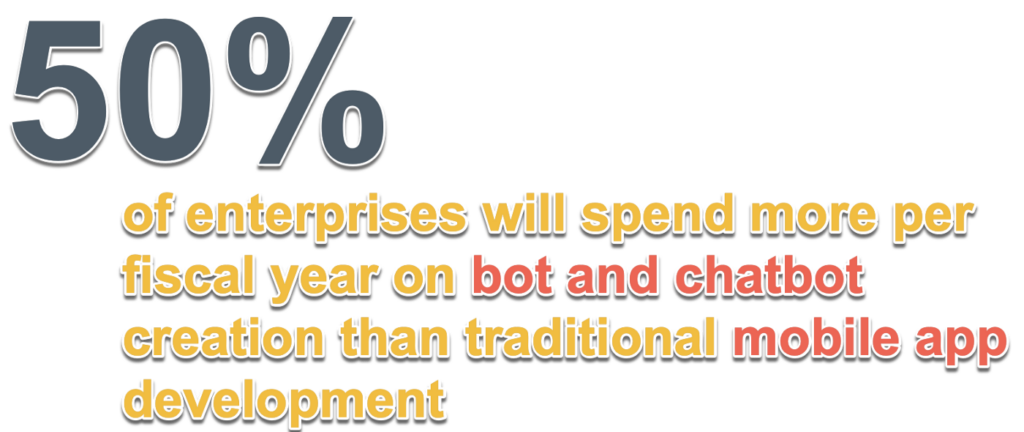
9. Customer intent must be aligned with business intent and needs to be decomposed to a low level.
10. When selecting use cases, choose the low-hanging fruit to give your chatbot the best chance of a successful deployment. Good use cases are high-volume, low-complexity, assisted-service inquiries, etc. Only once low-complexity use-cases are successfully implemented, review and prioritize the medium to high-complexity use-cases for deployment.
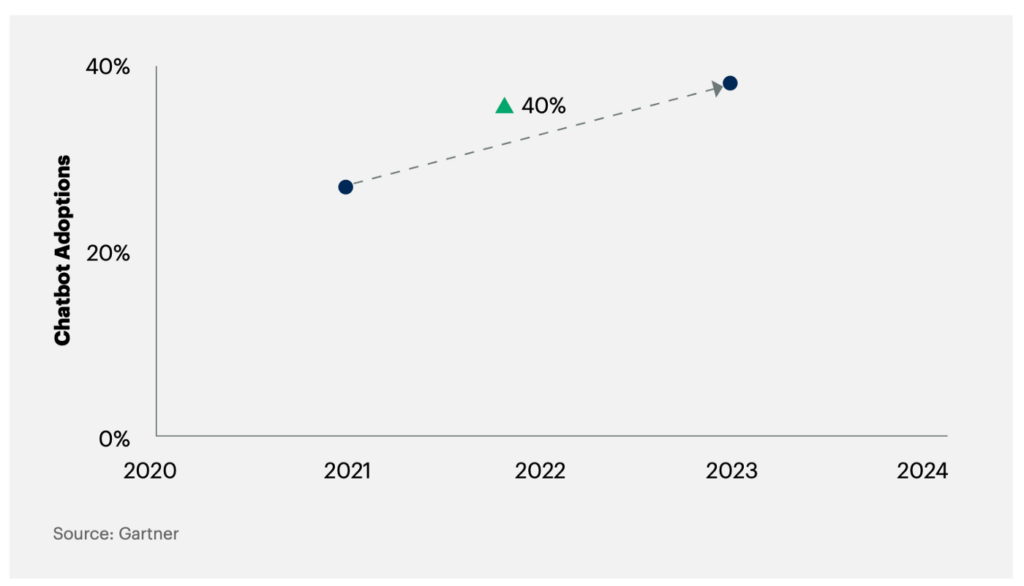
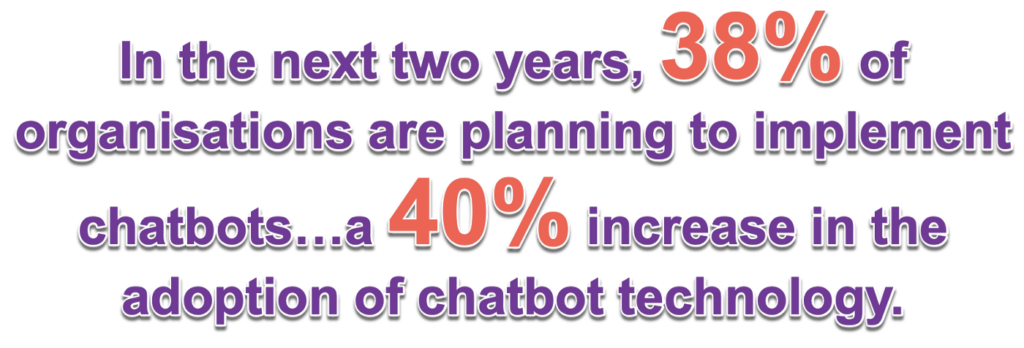
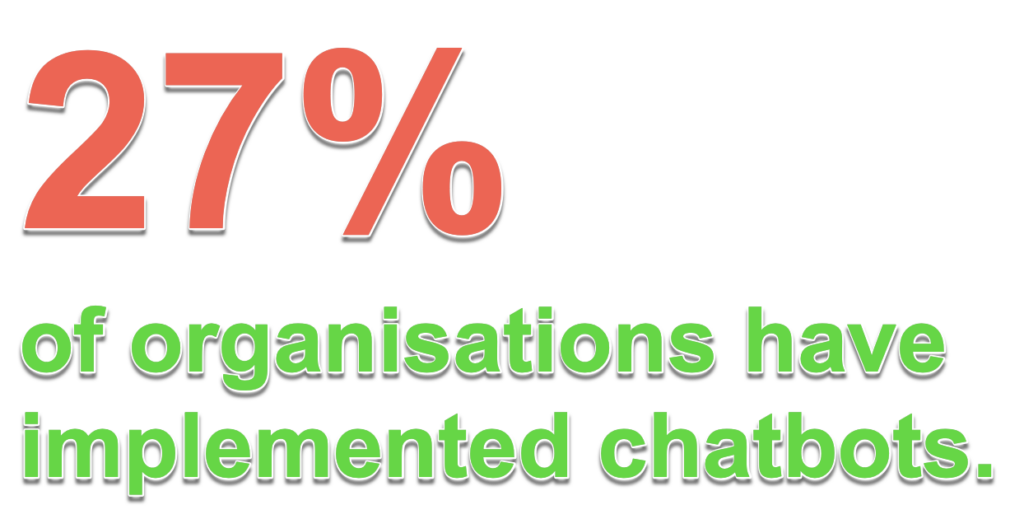
In the next two years, 38% of organisations are planning to implement chatbots — a 40% increase in the adoption of chatbot technology.
~Gartner

Customer Centricity In Chatbot Design
The chatbot design and workflow must be based on customer intents. The customer journey must dictate the chatbot functionality.
The chatbot flow needs to be:
Seamless — Understanding customer intent is key to customising the chatbot flow.
Customer-intent-specific content — Relevant and personalised content provides direction to the customer and conveys the notion that the organisation knows the user and cares.
Trust — Low-effort but highly secure authentication and authorisation mechanisms improve customer trust.
Consideration needs to be given to identify key stakeholders, supporting technology, operations, business requirements, security, risk, compliance, and data analytics, together with chatbot technology vendors.
The dependency list is a critical input for staffing and expertise requirements, estimating the cost, the implementation timeline, and the overall success of the chatbot deployment and continuous improvement. Gartner advises that organisations conduct this exercise in the initiation phase before committing to specific deployment timelines.
Conclusion
The popular approach to chatbot projects is to start with technology and compiling a comparison matrix for features.
Once the technology is determined, organisations work backwards to implement this technology. And determining the intents is very much a guessing game.
For successful chatbot deployment, analyze and define the chatbot applicability to the customer journey, and design the chatbot workflow based on customer intent.
~Gartner
Gartner emphasises that an organisation needs to start with defining user intents, followed by business intents. And subsequenlty create alignment between the user intents and the existing business intents.

User intents can be gleaned from existing user conversations like agent conversation transcriptions, IVR recordings, emails, etc. These user utterances can be clustered using embeddings. The clusters will be collections of semantically similar user utterances, hence constituting intents.
Subsequent use-cases can be defined, with CX goals. Making a technology choice at this stage makes much more sense, and how the chatbot will fit into the enterprise ecosystems. Dependancies are often related to integration for supporting API’s and medium integration. Mediums refer to where the chatbot will be surfaced, be it SMS, WhatsApp, Messenger, etc.
And lastly, select low-complexity use-cases that preferably generate revenue and save costs. Or high-volume, low-complexity, assisted-service inquiries, and lastly high-complexity use cases where a chatbot can be leveraged to augment assisted channel services.









