Save

Are you a designer? Maybe you’re a visual designer, a user experience designer, or a product designer. Or something else. It might be the case that you are not sure what to call yourself, or that you have difficulty explaining to others just what you do (which is even more difficult). I know I have a hard time explaining my design role(s) to others.
Back in the day we all were (just) designers. There was a time where an agency had a creative director, his team of art directors, designers and maybe an intern or two. If you take a quick look around the office today you see an ever increasing number of design roles. Next to the (visual) designers you have user experience designers, service designers and sometimes even something called unicorn designers. Not to mention cool new design roles like design ninja’s and magicians you see at startups.
Anyway. Let’s focus on designers, user experience designers and service designers.
Where did user experience and service design come from?
User experience came as a split from (web) design. Web design was too much about delivering visual work, advocates of user experience said. Most people credit Don Norman with inventing the term user experience back in the 80s. He believes that design is about more than just something that happens on a screen. It’s about the user’s physical location, the company’s services and the user’s opinion of it. I think he’s right. I believe most designers agree with him as well.
As stated on Nielsen Norman Group’s website; “User experience” encompasses all aspects of the end-user’s interaction with the company, its services, and its products.”
If you believe design is about more than just pixels on a screen, I can imagine that you create your own view on design and how it should be, just like Don Norman did. It makes perfect sense. There’s a problem, however. If you skip a few years since he came up with the term user experience, you now see that we’re back where we came from. Many job openings still ask for “UI/UX designers”. The actual job openings that ask for UX designers do not always ask for UX the way Don Norman intended. In many of the UX designer job openings, designers are expected to deliver pixel perfect design, prototypes and maybe facilitate a workshop or two. There hasn’t been a lot of change in the role, except for a new name. Companies still consider UX designers to be a combination of a visual designer and what a UX designer should be. Don’t get me wrong. I understand why that’s the case. One employee who can do multiple things is cheaper than having an employee for every detail you’re working on. It is just not what Don Norman envisioned when he came up with user experience. That’s why we’re seeing a new kind of design emerging; service design.
Yet another split. (Web) design was too much about pixels, so we moved to a new kind of design; user experience design. In practice, user experience design is still believed to be too much about pixels, so now service design takes the center stage. They use the same arguments; user experience is too much about visuals. It should be about more than what you can see on your screen. Service design is about working together with your users and stakeholders. It is about the customer journey, user research and touch points. Visual design has a lower priority for service design than it has for user experience or web design. Maybe service design is the way Don Norman wanted user experience to be?
Finding the designer’s balance
So, we started with (web) design. Now we also have user experience design and service design (and even more). Both of which came to life because they believed design was too much about pixel perfect visual design. User experience is mostly still about pixels where service design pays less attention to visual design, while using a holistic approach to the design challenge. Service design involves other roles as well, like marketing, business and IT.
It brings us to a question. Should design be about what you see on a screen? Or should we focus on everything else? Well… Design is about pixels on a screen. Just not only about pixels. It is a subtle balance between the screen and everything evolving around the screen. Great design is where business goals meet the user’s needs. That does include the screen. It doesn’t matter what you call the design role.
Designers come in different shapes and sizes. Some are called ’T shaped’, others are called ‘I shaped’ or ‘unicorns’. Maybe we should say designers are M shaped, or stop judging designers based on letter shapes all together. Sure, every designer has his specialty. You just can’t assume everybody has just one specialty (T shaped) or that his other skills are all on the same expert level (unicorn designer).
There shouldn’t be a different label for every individual designer. You’re a designer. You (should) possess basic skills to make your design stick. Those skills are the same, whether you call yourself a user experience designer, a product designer or something else entirely. You should be able to develop and facilitate design sprints and workshops, be able to do your research, validate your assumptions and be able to communicate and sell your design to your stakeholders. Don’t forget; you also have to be able to make an awesome looking visual design, whether it is a presentation, a user interface prototype or a research study. It’s part of your designer’s tool box.
Why are user experience and service design two different terms? Both consider themselves to be a holistic approach to design where they focus on the entire experience, not just the pixels on screen. In theory, user experience and service design are very similar. People just expect them to be something different because they have different names.
Design thinking
Whichever design label you give yourself, you’ll most likely use some sort of design thinking method as a way of working. There are many different forms of design thinking as well. Design thinking has the same problem as design in general. There are so many different design thinking labels. It’s very confusing. Design thinking labels show significant overlap as well, just like user experience and service design does.
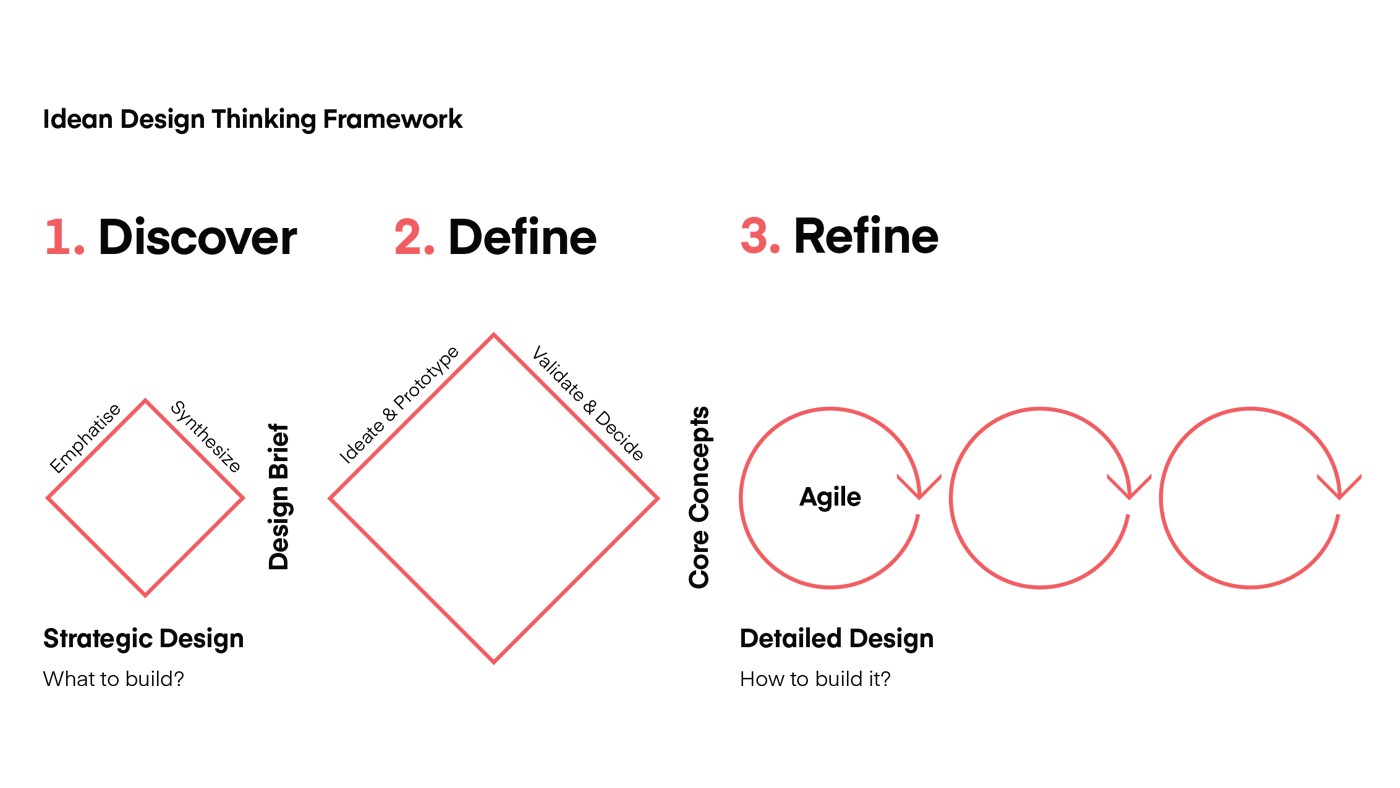
At Idean, we work using a double diamond visualisation of design thinking.
We work using three steps; discover, define, refine. It means that we start with collecting data and doing our research. We continue with prototyping during the define phase where we design different solutions and verify them. Once we have our core concept in place we continue during the refine phase. It’s a process of detailed design where we work in agile sprints to further refine and improve our concept into a full product.
Everyone at Idean can do the work using our design thinking framework. Even though we have visual designers, user experience designers and service designers in our ranks. We’re all designers, whatever kind of designer you call yourself. The designer’s tool box I mentioned before should be able to do the trick for the entire process.
Looking to the future
When looking forward to the future of design, I believe it is time to take a step back. We’re all the same. We’re all designers. A designer who can do anything. He can do his research and present his findings. He can validate and improve his work. He knows how to sell it. And last but not least; he knows how to make it look awesome. We’re all (just) designers after all. And that’s okay.
Nick is a designer with experience in UX, interaction and user research. He has worked as a design consultant in finance, healthcare and retail. As a designer, he believes design to be a holistic solution where the business’ goals meet the user’s needs. Nick currently works with Idean, Capgemini’s creative agency.