Save

The aesthetic bar for software design has been raised, and as consumers evolve to demand more out of products, businesses will be challenged by the tradeoff between product functionality and simplicity. I believe the most important hires of the next decade will be user-focused designers who are able to effectively simplify complex systems.
The market of software buyers has changed
Employees, not department heads, are today’s software buyers, and these users have sophisticated technology expectations based on their experiences with consumer-facing apps. Data suggests that the average mobile app loses 80% of its users within three days of download. The new users of enterprise software are fickle, and the window of time allowed for value demonstration is small and tightening.
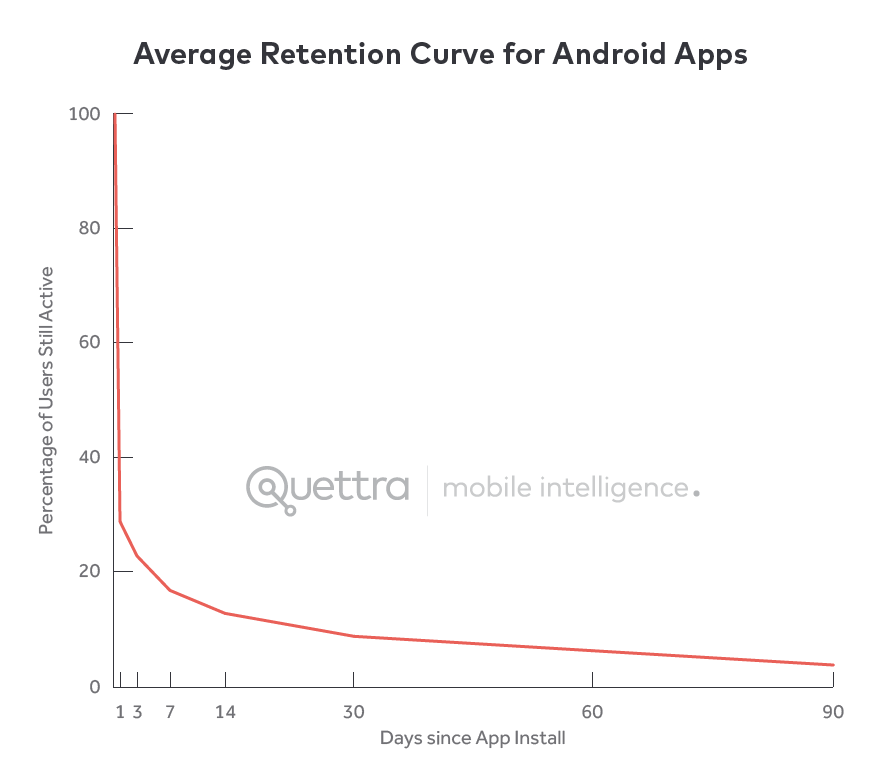
Average Retention Curve for Andriod Apps from @andrewchen
The average attention span today lasts just eight seconds — placing our concentration as a species lower than that of goldfish. We are distracted beings living in a distracted world, and for businesses to stand out in the competition for our attention, first impressions matter.
When evaluating a website for the first time, people form opinions in 50 milliseconds. Buyers of software products baseline product quality in a fraction of a second, and understanding this distinction has become critical for software firm strategy.
The defining software companies of the past decade have understood the importance of design simplification, and users have been the beneficiary. As product functionality grows, simplification suffers. Repackaging complex systems into user-friendly interfaces is a challenge that all businesses must address. As Joe Sparano notes, “Good design is obvious. Great design is transparent.”
The new buyers of software are quick to judge and hard to impress. In order to cater to this shifting demographic, the most talented people within an organization will be those tasked with making the most out of 50 milliseconds.
Competition has forced a change in strategy around product distribution
Open-source resources, cloud-based solutions, and APIs have significantly reduced the time, capital expenditures, and steps necessary to start a business. This availability of resources has driven the number of business applications up and to the right, and the saturation of businesses has resulted in an environment that favors the consumer.
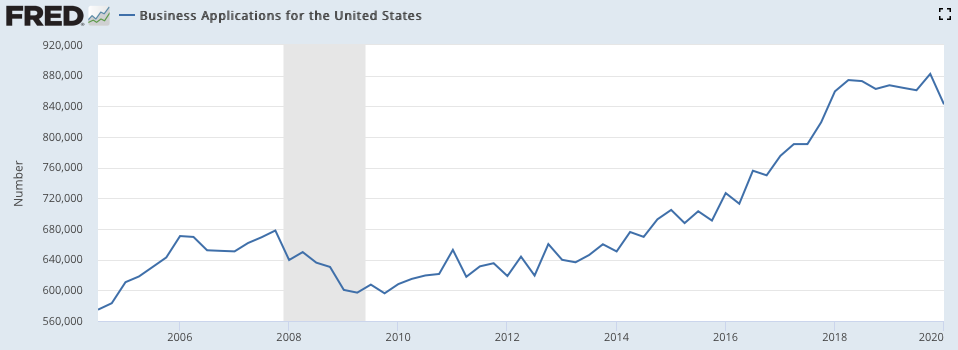
Business Applications for the United States fromFRED
Despite being easy to start, startups are more expensive than ever to grow. Heightened competition has made it more difficult to reach new users, and ad-based spending has skyrocketed. Conditionally, a war on price has ensued, resulting in a race to the bottom on pricing and a race to the top on ad spend.
In order to justify the rising costs necessary to acquire customers, products must extract more out of customers. However, in a world of seemingly limitless alternatives, defending price hikes has become more difficult. The traditional method of monetizing through ads contradicts good product design. Consumers have been vocal about their hatred of ads, and monetizing through page distractions sacrifices a seamless user experience.
A flooded market has made it more expensive to capture new users, and organizations must rethink their business models to readjust with this change.
Freemium models have become standardized as consumers need to play around with software before agreeing to pay for it. Companies like LinkedIn, YouTube, Dropbox, Spotify, Tinder, Notion, and Figma have demonstrated the upsides of providing freemium services, and I expect many others to follow similar playbooks. Freemium versions provide easy customers and increased brand equity, but offering your product for free comes with challenges.
From a design perspective, the lack of a usage barrier places more emphasis on the presentation quality of your product. Supporting unpaid users is the fatal flaw of the freemium model, and the challenge for product teams is to provide enough of a glimpse into the usage of a product without giving away so much that non-paying users never convert to paid. As demonstrated earlier, creating a product that people continually use is incredibly difficult; designing a free product that becomes sticky enough to persuade users they need to pay is an even more daunting task.
Reaching a critical mass of users can no longer be engineered through proprietary code and traditional sales methods. Selling up an organization requires an added emphasis on product design, and I expect an increase in organizational resources to fill this void.
Structural changes are coming
The traditional organizational structure has hindered great product development by placing product as an afterthought.
The typical sales-led business can be separated into two departments: the profit center and the cost center. The profit center includes sales, marketing, and success teams, and their sole purpose within the organization is to bring in new logos and service existing accounts. The cost center encompasses the engineering and product teams, and their mission is to develop and iterate software that caters to its clients needs and requests.
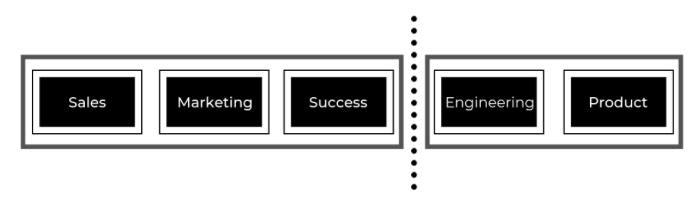
The problem with separating an organization into two separate parts is that the goals across departments do not align. Leading with sales and following with product tweaks forces organizations to prioritize high-volume accounts and minimize the amount of product tweaks necessary. If and once a large account is signed on, there becomes pressure from the board and employees to only go after similar-sized accounts afterwards. This type of strategy encourages against iteration and instead incentivizes growth without understanding engagement, and this recipe equates to dissatisfaction and churn over the long run.

Photo by ThisisEngineering RAEng on Unsplash
From an investor perspective, the increasing importance of design has overarching effects that will change their internal evaluation process.
Venture capitalists work with limited data points and historically have relied on a number of metrics to gauge the quality of a given deal. Recurring revenue, churn, headcount growth, and a list of other figures are assessed in the due diligence process, but many of these frameworks are outdated and overused.
How good of an indicator is headcount growth if the best companies are able to grow organically? How good of an indicator is revenue if freemium models have not been harvested long enough for users to convert to paid accounts? Qualitative information is even tougher to understand. Good design is aesthetic, and understanding inconsequential details of product design will have to be taught and learned.
Good products sell; great products sell themselves. They build trust with customers, fuel organic growth, and foster a brand that obtains repeat purchases. Design is the next moat, and founders and investors will need to adjust their evaluation frameworks to reflect this change.
This article was originally published on Medium.
Clay is a junior venture capitalist at a fintech-focused fund. He invests primarily with pre-seed and seed companies, and he spends his days critiquing and refining pitch decks of the companies he works with.







