If you’re about to design a new product or to expand it to a new market, leave your assumptions aside: focus on your users first.
Between awesome features, branding colours and business goals, users, who should be the main prioriy, are often forgotten during the process. This is even more highlighted when designing for international target groups, where users’ cultural background may be neglected.
Let me tell you a quick story about the misconceptions about the user’s behaviour:
Some years ago an airport took notice that the elderly travellers were spending a lot of time in the toilets. So much so, that they almost missed their flights. Consequently, they decided to redesign the facilities.
The immediate thought was apparently obvious to all: holding on your most primordial needs gets harder with age. So the solution came: getting more toilets on the way to the gates so the elderly would not have to walk for too long, and so spend more time on the way to the toilet.
Not long after, the implemented solution did not seem to bring any results since the same incident kept happening. The airport decided then to hire a design consultancy to redesign the space and find the best way to deal with the ongoing trouble.
Long story short, the design consultancy convinced the airport to spend a few days doing user research in the field to better understand the hidden problem(s). Ready for the outcome of the story? Turned out that the reason why the elderly kept going to the toilet had nothing to do with nature’s call, but rather the fact that they needed to listen to the loudspeaker announcements about flights’ gate, schedule, etc. In the airport, open areas and corridors are so noisy, that they needed to go to the toilet to be able to listen to it, since it’s usually a quiet place.
What could have been a quick and simple process turned out to be a long and intricate one because the premises of it relied simply on assumptions.
Don’t underestimate user research
Look at the example of the world-wide famous Starbucks when expanding to Australia: the northern american chain decided to open their business in Australia in 2000 and by 2008, it had 87 open stores. The company started getting major losses immediately since they didn’t take into consideration Australia’s coffee culture. Rather than sugary drinks, Australians enjoy coffee in a different way, more similar to Italians and Greeks, preferring products like a flat white or an Australian macchiato. Nowadays Starbucks still exists in a few places in Australia, however, it is mostly to fulfill the needs of tourists that are already familiar with Starbucks from their home countries.
When bringing a new product or when expanding a product to a different culture than your own, you must consider the users’ background as essential.
Mind users’ cultural background
Being aware of the users’ cultural background is a first sign that the project is going in the right direction. Adjusting a product to a new audience requires knowing who the users are, their needs, goals, pain points and overall culture. As much as we might live in a connected world, where information crosses the globe in a glimpse of an eye, we should not disregard that there are particular characteristics and differences in each culture. That’s a key factor.
For many of us, the place we live in defines a big part of our culture and identity. To different people, this notion may vary to different extents: your culture might be related to your country or your local community. Culture crosses concepts such as language, religion, social habits, geography or even gastronomy.
Without a doubt, having in mind currency and language adjustments is crucial. However, you should dive deeper:
- understand the different symbols that define your target group;
- make a research in order to get the cultural insight that will bring relevance to your business.
“Don’t find customers for your products, find products for your customers.”
Seth Godin
Addressing cultural differences
Nowadays, there are more innovative companies that take into consideration their users’ needs. Depending on your user research insights, you might need to rethink your business model for a specific country or adjust a few key elements here and there. What’s important to highlight is that the insights gained from research will be extremely valuable. Those will help you decide which approach to take.
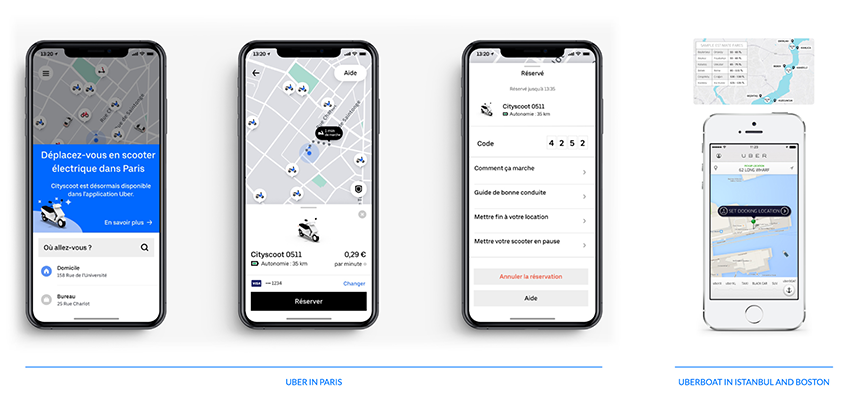
Uber is the example of a company that did not just copied their ridesharing app throughout the world, but rather thought of the cultural needs of each city and country they expanded to. In Paris, Uber decided to create a collaboration with Cityscoot in order to add scooters to their existing fleet. In a constantly moving city, providing more flexible and easy to use alternatives is a way to adapt to the local habits. Besides Paris, Uber is also adapting to the transportation culture in Istanbul by allowing the users to book an Uberboat (operated by the local company Navette), as a way to run away from the car and railway traffic that inflicts the city.
Follow a Product Design Process
Think about your latest projects. What could you have done differently? If you’re planning to create a web or mobile app from scratch or to scale an existing product, there are some key elements you should keep in mind before taking any action.
- First and foremost: the process! Like I’ve been preaching in the past lines, the way to embrace this cultural move is essential. Adopting a user-centered design process is the best way since you will be using a methodology that focus, just like the name says, on the user (and what else have we been talking about if not users?).
Here at Imaginary Cloud, we felt the need to create our own Product Design Process (PDP). It’s a user centered design process with a special focus on digital products. We gathered in multiple steps the following phases: Research, Ideation, Execution and Technical Assessment.
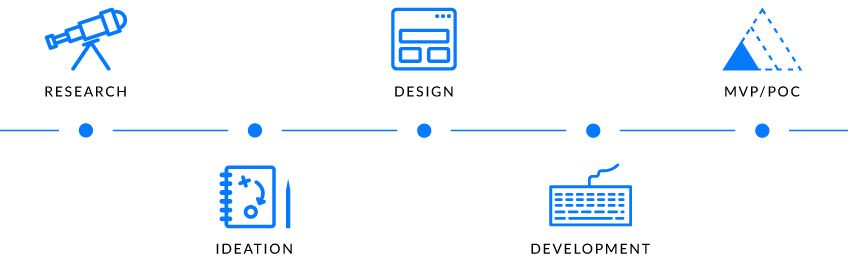
The first stage, Research, is what I’m focusing on at this moment. During our user research, one of the most important methods is the “Personas”. Overall it helps us, as a design team, to gather insights about several individuals with the same end-goals. In essence, to define them we should understand their demographic information, user context, goals, needs, frustrations and behaviours. There are different persona methods to adopt depending on the goal.
When doing the user research, we create the personas, but it’s way more than that: we’re generating empathy with users by collecting insights and moving away from assumptions (that later on can cause friction in the user experience);
- Besides the user research (that may include fieldwork), it’s important to also have your own literature research. There are a lot of books, papers and specialized magazines, where we can find answers to some of our questions. We don’t always need to reinvent the wheel as sometimes it just might slow down a process that is actually quite simple. It’s part of the work to keep ourselves informed and engaged, by searching for the right sources and content;
- Invest time and efforts in your product’s UI/UX design. Keep a sharp eye on the layout, style, font, colour and imagery as these are elements closely linked to your initial user research. We go through these parameters one by one during our design process:
When we follow our PDP, in the Design Benchmark phase, we take a look at the ecosystem where your product fits. We analyze what are the existing products, look at the best market practices and identify what can be brought to your product that increases its value. It’s important to check on other products’ features, understand where they are regarding value and communication style, as well as their information architecture.
- Another useful tool is the moodboard. Here we get to explore the visual aesthetics of the product, having in mind all the background we bring with us (user research, personas, decision matrix, as many other more). Plus, it’s a moment to reflect upon how the values and emotions of such a target group will be visualized and turned into images, colours, fonts and overall style. Later on, this will help the design team build a style guide and graphical user interface that is comprehensive and matches the user’s background culture.
- Keep in mind that the language is equally crucial in your product: the font type, size and length matter. When creating a product, designers should take into account that different languages have different lengths. Sometimes, they need a different layout for that particular language.
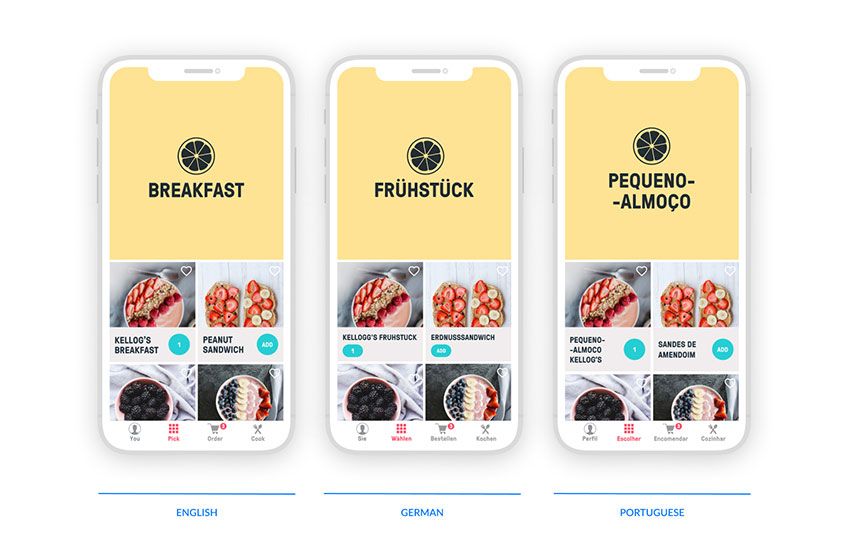
Besides that, when it comes to translation, we do know Google’s tools are incredibly useful (like Google Translate) but they don’t make miracles (not yet, at least!). So don’t underestimate the value that a local translator can add to your product.
- For a moment, instead of thinking about the user, let’s actually try to focus on the design team behind the product. After all, they’re the ones designing it. If we don’t incentivize a multicultural environment, the product might still be dragging a handful of assumptions about the user’s culture and context. It’s important to have an open minded team that is empathetic towards the users and that can bring their own cultural background as a plus to the project. In fact, according to the Catalyst “teams are as much as 158% more likely to understand target consumers when they have at least one member who represents their target’s gender, race, age, sexual orientation, or culture.”
- Consider allocating a specific part of your budget to user research as such investment will bring you beneficial results in the long-term. It’s often perceived that it’s preferred to skip the user research stage not to exceed the project’s budget. However, that’s not necessarily true. Cutting corners has often proved to lead into trickier paths rather than brightful ones.
Aligning your product with your users’ values, needs and frustrations right from the beginning is the best way to predict and achieve success.
Why a cross-cultural design is vital to your web or mobile app
Cross-cultural design is definitely a milestone along the process.
Throughout this article I’ve been sharing a few essential tips about user research methods, as well as other relevant ones. Hope these will help you throughout your journey in bringing a product into an international audience.
Start by understanding that user research is beneficial in many senses: by not underestimating your target group you’re halfway through success. The design team may complement this research with its own literature references to keep themselves informed and engaged. After these steps have been checked, the design team may gain more insight by analyzing where your products stands, by making a competitor’s check and finding market’s best practices with the Decision Matrix.
Further along the way, translating the insights from user research into the look and feel of the interface is done through one of our methods, the moodboard. But don’t forget that besides the colour, font type, imagery, style, etc. there’s an important element which is the language your product is being translated to. Having that in mind is crucial since it may affect the design interface and require a local translator.
The team behind the product plays a big role in it, after all, they are the ones architecturing the product. The more multicultural and inclusive the team is, the more likely it is they will understand the users they’re designing to.
Besides the previous tips, the budget might still be going around your mind. Do not fear, if you want a successful product invest in user research and bare in mind that knowing your users’ values and needs will bring purpose to your business.








