Save
In his iPhone Resolution video, information design expert Edward Tufte praised the information density and content resolution of the device. Known for evaluating Web interface designs by counting the quantity of links present, Tufte is a big proponent of clarifying information by adding detail, not “computer administrative debris.”
In his iPhone Resolution video, information design expert Edward Tufte praised the information density and content resolution of the device. Known for evaluating Web interface designs by counting the quantity of links present, Tufte is a big proponent of clarifying information by adding detail, not “computer administrative debris.”
Computer administrative debris reduces information resolution and steals content space away from the user. The iPhone brilliantly suppresses much admin debris. The idea is that the content is the interface, the information is the interface, not computer administrative debris.
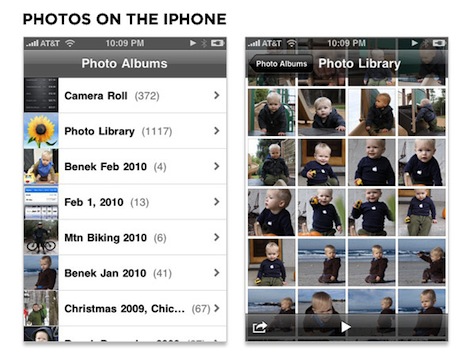
In particular, Tufte called out the iPhone‘s Photos application as an example of clarifying information by adding detail. “In this collection of photographs, many information elements are arranged on the same surface as the user scans 150 images arranged in a two dimensional small multiple format.”
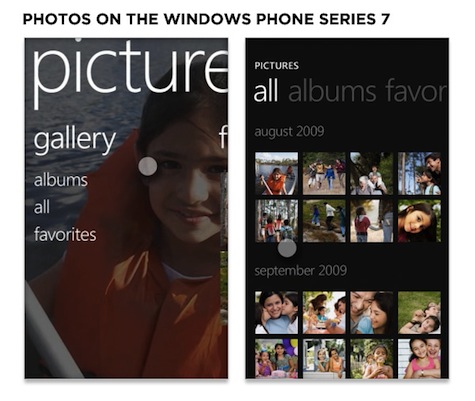
With this in mind, it’s interesting to compare the information density of the iPhone’s photos experience with Microsoft’s Window Phone 7 Series experience. The iPhone’s first screen concisely lists available photo sets and with one tap drops people into a dense grid of images where the user interface is minimal and transparent enough to enable the entire screen to display content.
The Windows Phone 7 Series begins with a top-level navigation menu consisting of three options. A quick tap on “albums” brings up a similar listing of images but with substantially more interface elements. It’s also a bit unclear if all the pictures in an album will be listed in this view or if another tap on the album title is required (adding a third step to the navigation process).
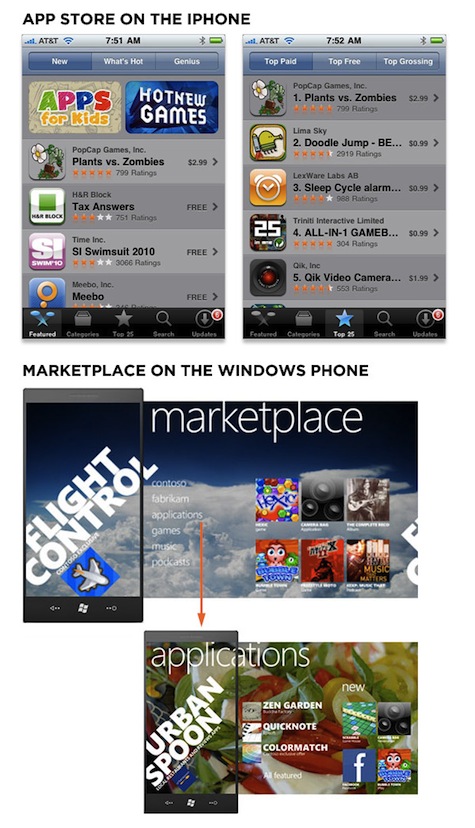
The differences in information resolution between the iPhone and Windows Phone are even more stark in the application store features. In addition to seven ways of finding and filtering apps, Apple‘s App Store displays four apps complete with icon, title, publishing, average rating, number of ratings, and price.
Marketplace on the Windows Phone features one application with an icon, title, and one-line description. One touch gesture (drag/flick) later, there’s a menu consisting of six items. Tapping on “applications” takes you to another featured application. One more drag/flick and you are finally seeing three applications you can download. Contrast the amount of information present on this screen (the fourth in the process) with the amount shown on the iPhone’s initial App Store display.
It will be interesting to see if these differences in information resolution have an impact on the overall user experience of using the Windows Phone 7 Series.
While the Windows Phone 7 Series user interface may not be optimized for high information resolution, it does make interesting use of teases and transitions, which I wrote about today.
This article was originally posted on Luke’s blog, Functioning Form.
Luke Wroblewski
LukeW is an internationally recognized product design leader who has designed or contributed to software used by more than 700 million people worldwide. He is currently Chief Design Architect at Yahoo! Inc. where he works on forward-looking integrated customer experiences on the Web, mobile, TV, and beyond. Luke is the author of two popular Web design books: Web Form Design (2008) and Site-Seeing: A Visual Approach to Web Usability (2002). He also publishes Functioning Form, a leading online publication for interaction designers. Luke is consistently a top-rated speaker at conferences and companies around the world, and is a co-founder and former Board member of the Interaction Design Association (IxDA). Previously, Luke was the Lead User Interface Designer of eBay Inc.'s platform team, where he led the strategic design of new consumer products (such as eBay Express and Kijiji) and internal tools and processes. He also founded LukeW Interface Designs, a product strategy and design consultancy, taught interface design courses at the University of Illinois and worked as a Senior Interface Designer at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA), the birthplace of the first popular graphical Web browser, NCSA Mosaic. Visit Luke's website: https://.lukew.com/ Or his writings at Functioning Form: https://.lukew.com/ff/ And follow Luke on Twitter: https://.twitter.com/lukewdesign