Save

The pros and cons of the persona
Getting through the user research phase of a design project can seem daunting, but in reality it’s just the beginning. When you and your team get to reviewing and synthesizing your research, you’re getting ever closer to bringing your concept to life. Usually, one of the first steps post-research is to create personas.
Personas give you and your team an overview of a user or a group of users. They also outline high-level assumptions about your user’s preferences and their behaviour patterns.

An example of a completed proto-persona highlighting motivators, behaviours, and needs for a single archetype. Leah Buhley, 2013, for Rosenfeld Media.
As a tool in a designer’s toolkit, personas nudge us to perceive a possible user’s situation with greater empathy. They also spark fresh thoughts about how a product or service could be used. For digital products, a focused, task-based persona can be crucial during these initial stages.
However, if your team’s aim is to understand what your users need, personas aren’t the most effective tool. Personas alone can’t reveal how users would behave, and the contexts where they might use your product or service.
Ideally, methodical user research results in many artifacts that inform your design team’s understanding of your users. Other research tools include: customer journey maps, service blueprints, empathy maps, emotional journeys, and user stories. A combination of these methods will often lead to the best results.
Personas are great for ‘humanizing’ users, and for painting a picture of individual experiences within an archetype. However, you shouldn’t rely on them to define what larger demographic or affinity groups—especially diverse ones—might want. In these cases, analyzing a larger dataset of behaviour patterns and contexts makes the most sense.
Understanding users on a behavioural and contextual level
The Jobs-to-be-done (JTBD) approach is a framework that focuses on how users “hire” those products and services that help them complete a task or meet a goal. JTBD frames all design requirements around how users functionally use a product or services. So instead of referencing static, presumptive, and homogenized demographic or affinity group descriptions that come with personas, you’re focused on outcomes a user wishes to achieve.
Here’s an example of framing a user need with JTBD for a digital task-management and note-taking product, like Notion or Evernote:
Job statement: The user’s key task, which they are hiring your product/service to accomplish
e.g. Keep my project notes organized when I’m on a tight deadline
Outcome statement: The user’s wants or expectations (outcomes) from using your product or service
e.g. Reduce the chances that I miss a deliverable for a project.
Since living, breathing humans are always changing their perceptions of their challenges, goals, and tools, it’s crucial to frame their needs in a fluid way, too.
Jobs-to-be-done is a perfect tool for this sort of framing, because it focuses on a user’s context and goals, rather than less-informative and generalized demographic or affinity group information.
Simply put: people are trying to solve a problem by using your product or service. Understanding what problem they’re trying to solve is far more effective than generalizing a non-task-centric group they may belong to. Knowing what they need to do is far more actionable information than assuming you know who they are by following a persona or archetype that can only hope to resemble who they may be.
Go deeper by mapping user stories, states, and contexts
Some other great frameworks to consider as you work to improve you and your team’s understanding of how people might want to use your product or service are user stories and user states and contexts.
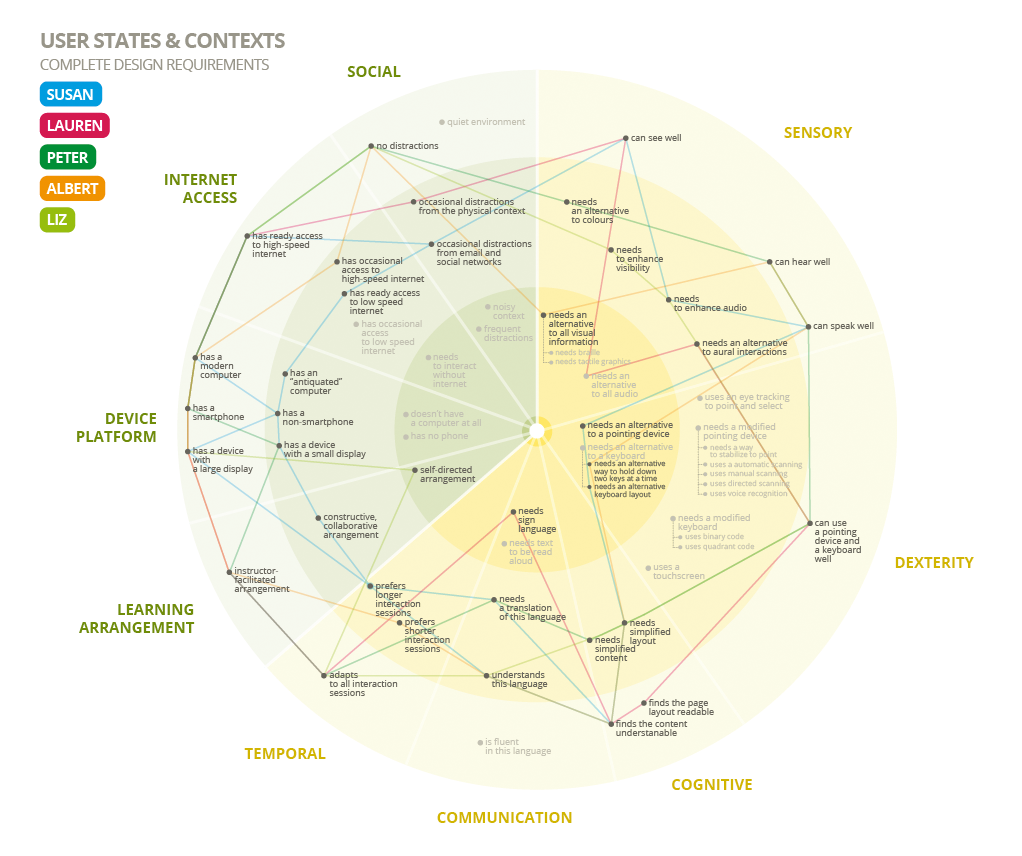
A user states and contexts map visualizes all of the requirements and needs that users experience. Image from the Fluid project.
Moving from research to product and service refinement
Testing and refining all of the methodologies listed above will extend and deepen your understanding of your customers beyond the limitations of personas.
As you evolve your approach, patterns will emerge in your observations, and you will become adept at weaving them into design requirements.
Longer-term, you can expect to see significant benefits from this approach:
- more effective design requirements,
- better prototypes, and
- better-informed design teams operating with more empathy after understanding the needs and outcomes of real users.
The path to effective service models and products is to deeply understand your user’s contexts and needs and the outcomes you can provide to meet those objectives. The tools and frameworks we’ve outlined here can leverage your user research into JTBD and user context maps, which will seamlessly direct you into more efficient product and development strategies.
Kate is a multidisciplinary designer, working across interaction design, user research, and service design to deliver inclusively-designed products and services.
User research, as well as a love for experimentation, drive Kate’s design process. She enjoys breaking down systems, and exploring tactics to improve experiences in unconventional ways. This work is all underpinned by human-centred principles and working laterally across disciplines.
You can follow Kate on Twitter @kate_matesic and find more product insights from her on Say Yeah’s Digital Insights blog.







