Save

Operator Overloading??… Hmmm. Isn’t this a programming concept?
True, this term does come from the world of software engineering, and I doubt it shares too much of an overlap with what I’m about to talk about here.
Regardless this was the most succinct way I could think of to summarize the approach that I’m going to talk about in this blog.
TLDR;
Operator Overloading in this context is a brainstorming approach when coming up with product ideas(specifically when thinking of ideas along the lines of AR, IoT, and wearable technology). It involves looking at the steps involved in the current process, identifying the body parts or tools(referred to as operators) that are at work in each step of the process, and thinking of ways to improve upon these operators to simplify the process.
This is something I thought of in a whiteboarding workshop at my university(Be sure to check out the Design Coterie student organization at IUPUI). In the workshop participants were given design prompts to ideate upon in short spans of 30–45 mins. I along with a few colleagues of mine tried out this technique to come up with a small set of prospective solutions to the design prompts handed to us.
So how does it work?
The approach is quite straightforward but often provides a handful of results if done correctly. The steps taken in this approach are as follows:
- Jot Down the steps involved in the current process
- List the operators in each step. An operator can be any object or tool that performs any action or is involved in any capacity in that particular step.
- Make a collection of all the operators from the previous step.
- Try to think of optimizations for each operator.
Operator Overloading in action
Let’s take a look at some use cases of this technique. The examples below are a dumbed-down version of the technique to illustrate how it works and the results one can expect from it. Ideally, the number of operators involved in any prompt would be far higher and thereby would open the doors to many more concepts.
1. Prompt: Design an iPad case for a doctor’s office
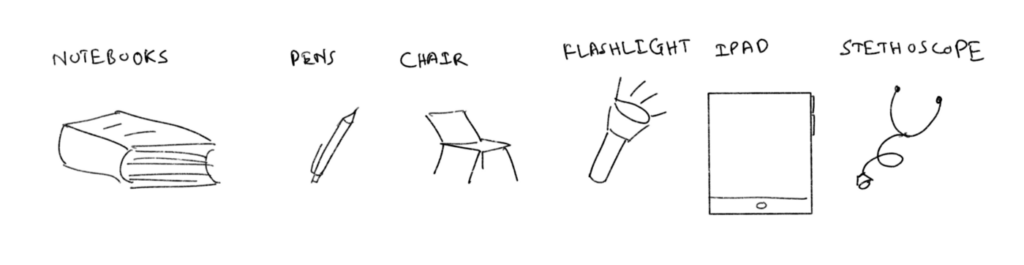
— Operators Involved: notebooks, pens, chairs for patients to sit in, beds for patients to lie on, flashlights, stethoscopes, etc
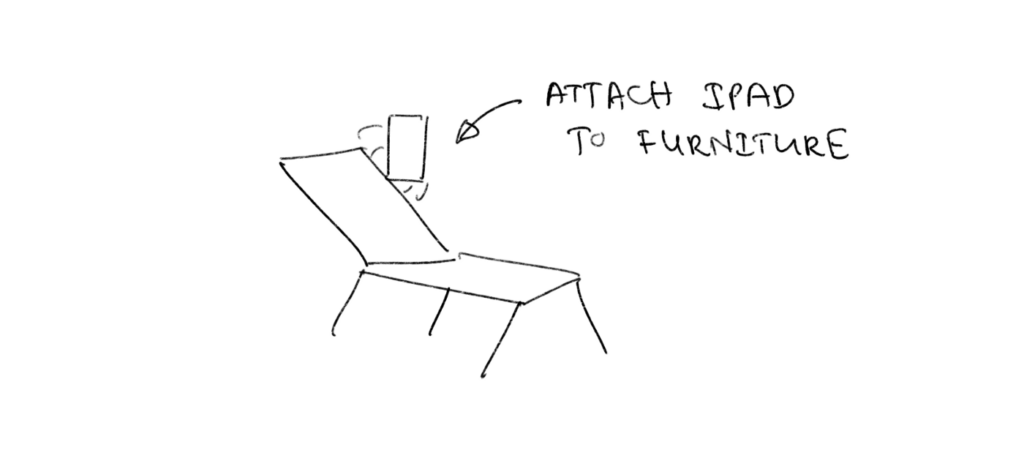
— Optimizing Furniture: ann iPad case with a magnetic attachment that would allow easily attaching it to chairs beds, etc
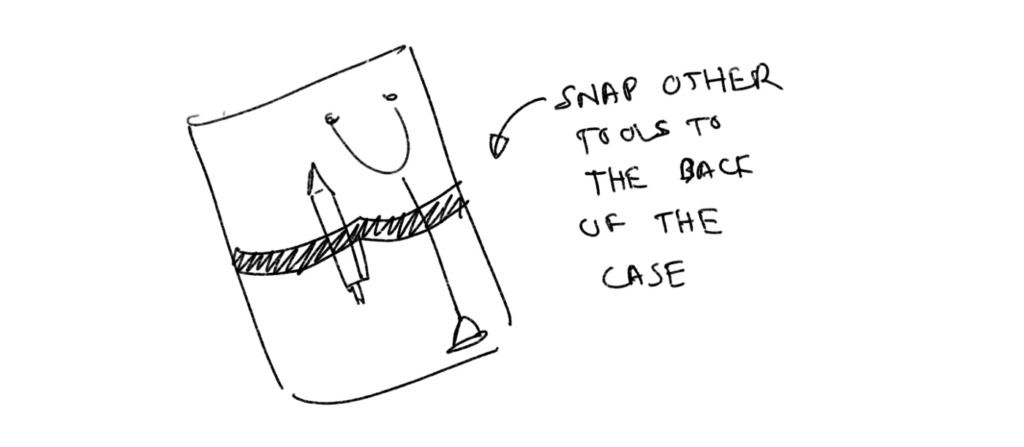
— Optimizing Tools: case with holders to attach commonly used tools stethoscopes, thermometers, etc
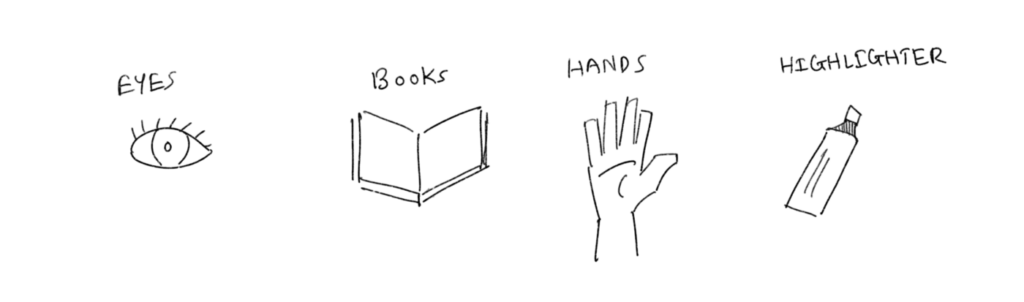
2. Prompt: Design a better way to remember which page you are on in a book
— Operators involved: eyes, books, hands, book covers, highlighters
— Optimizing eyes: smart glasses, that have an inbuilt camera that notes down the last page you read
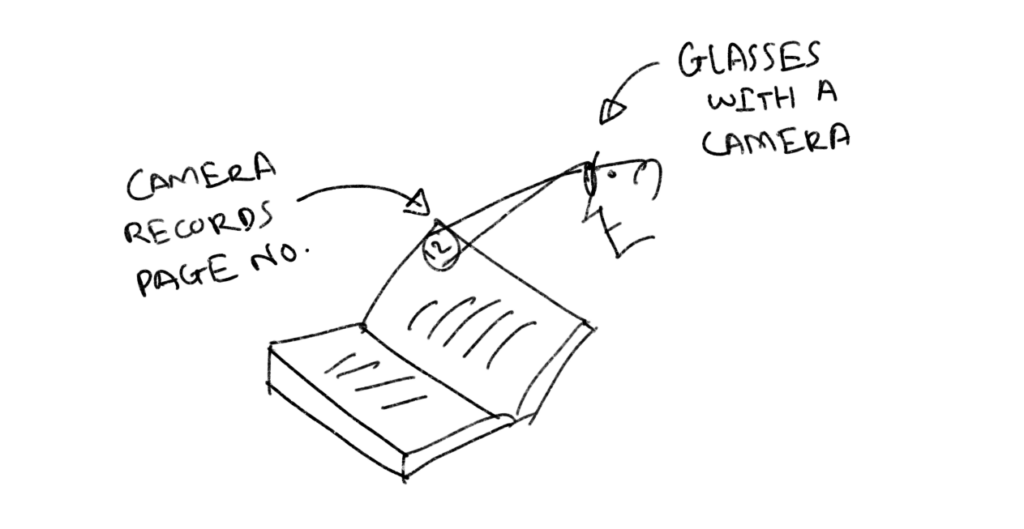
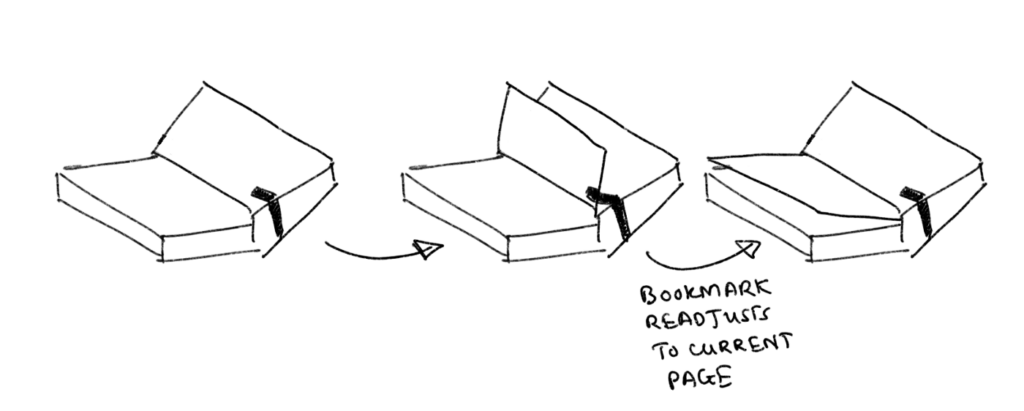
— Optimizing Books: an attachment with a thin bookmark that can easily be moved by the movement of a page. Whenever the reader turns the page, the thin filament bookmark would automatically be applied to the page currently being read
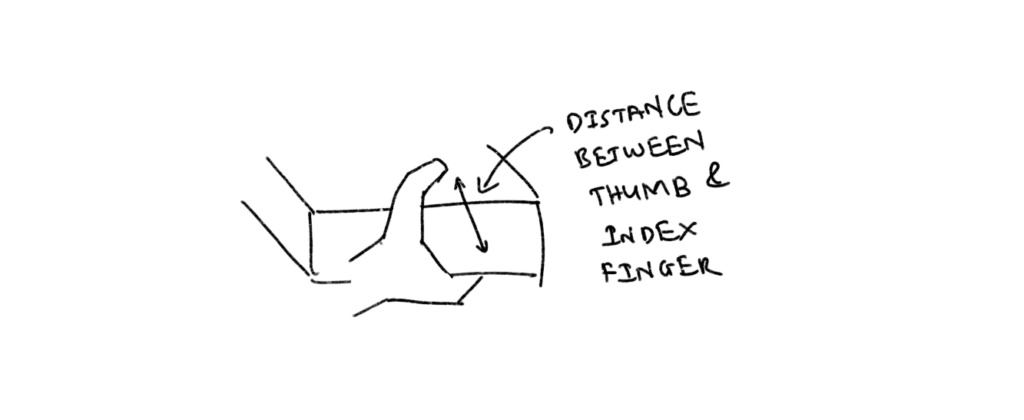
— Optimizing hands: gloves that can detect page number from the distance between thumb and index finger when the book is being held.
3. Prompt: Design an easier way to carry groceries without a car
— Operators involved: hands, bags, groceries, legs
— Optimizing hands: A grip with hooks. The plastic bags cut through the skin disallowing carrying heavy loads. A grip that can be more ergonomic and can be held more easily would allow carrying heavier loads
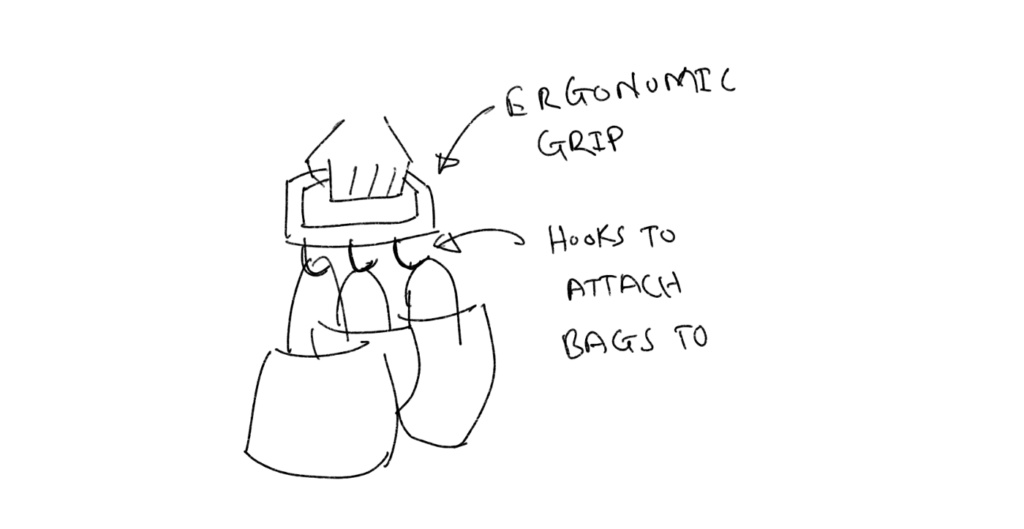
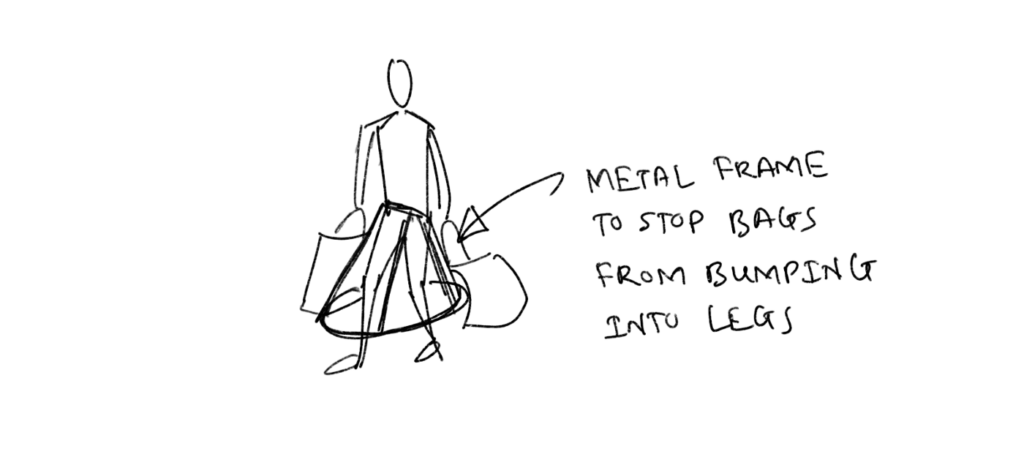
— Optimizing legs: One pain point is the bags bumping against legs which disallows running or walking faster. Or it can just be annoying. A hip attachment that keeps the bags away from the legs can improve the experience of carrying bags for long distances
Final Thoughts
In any brainstorming process, it is often a good idea to think of as many ideas as possible in the initial stage. The more the ideas the better. Narrowing down and refining the ideas can take place in the subsequent stages of brainstorming where ideas can be critiqued for their desirability, viability, and feasibility (Check out the Walt Disney method for brainstorming)
While the ideas generated using this technique might not always be optimal, they can serve as a good starting point in the initial stages of ideation and can also be built upon to build actual solutions to problems or even to conceptualize some kick-ass solutions in whiteboarding challenges
Peace! and Happy Designing 🙂
I am an aspiring UI/UX/Product designer pursuing my Masters in Human Computer Interaction at Indiana University. I worked as a front end engineer for around 6 years before switching to design as my primary field. "Design is intelligence made visible". This quote by Alina Wheeler perfectly encapsulates my outlook on design. I believe that good design can not only be effective in solving problems but also in helping businesses grow. In my free time I like to sing, sketch and accumulate dad jokes.
-
The author identifies the term “Operator Overloading” in this context as a brainstorming approach when coming up with product ideas.
-
The steps taken in this approach are as follows:
- Jot Down the steps involved in the current process
- List the operators in each step.
- Make a collection of all the operators from the previous step.
- Try to think of optimizations for each operator.
-
The author gives 3 examples of “Operator Overloading” in action:
-
Prompt: Design an iPad case for a doctor’s office.
-
Prompt: Design a better way to remember which page you are on in a book.
-
Prompt: Design an easier way to carry groceries without a carю
-
-
While the ideas generated using “Operator Overloading” technique might not always be optimal, it can serve as a good starting point in the initial stages of ideation.







