Save
This article covers 3 conditioning techniques designers use to influence behavior. These methods are widespread and employed in almost every successful app. Use with caution.
1. Classical conditioning
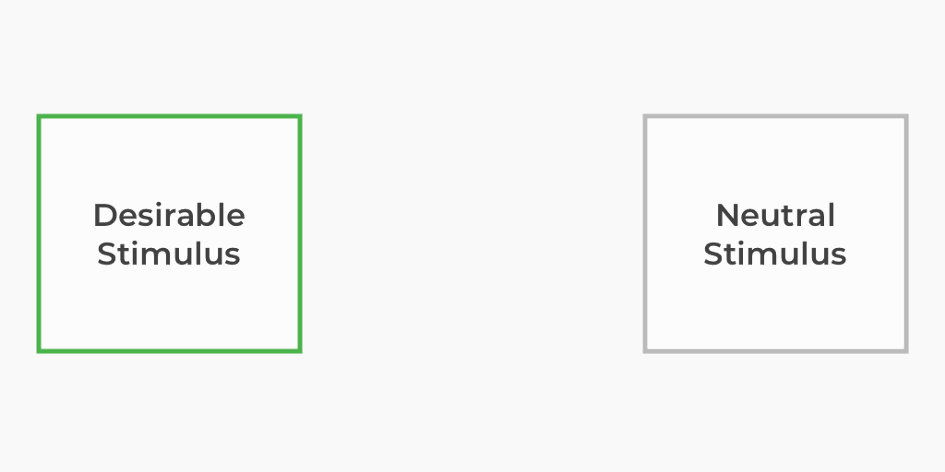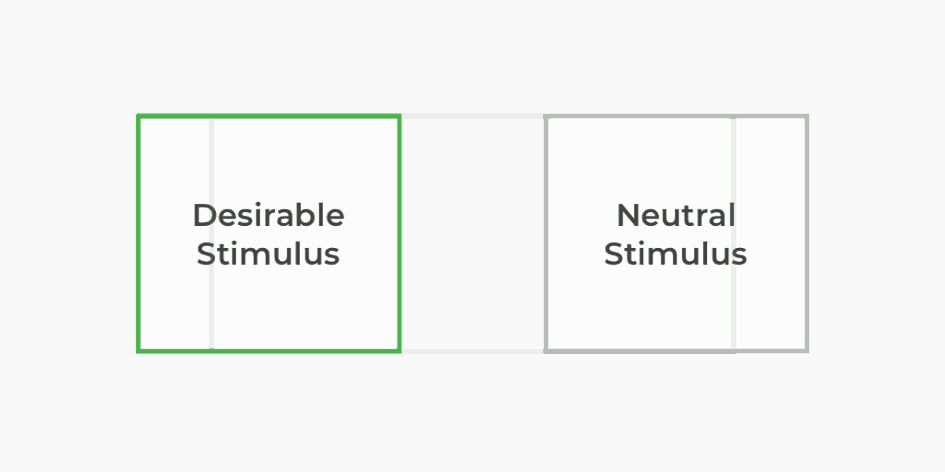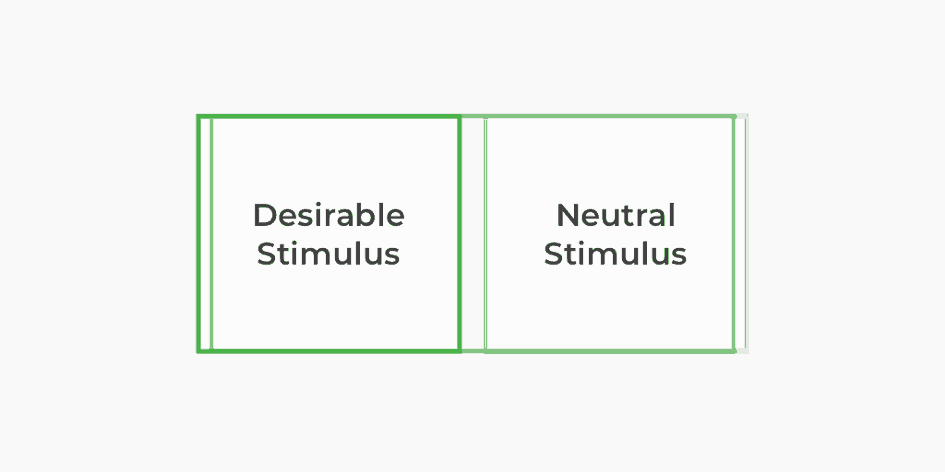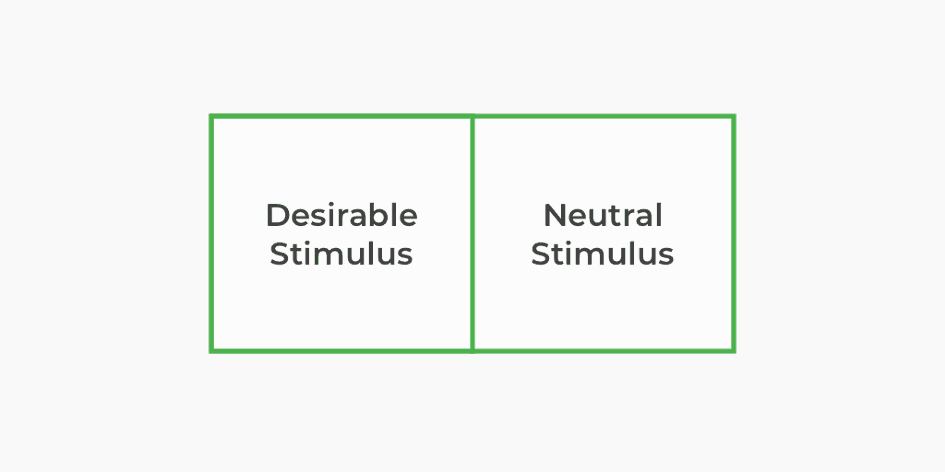
Classical conditioning is a subconscious association technique that pairs a neutral stimulus with a desirable stimulus to create an associated trigger. After many successive pairings throughout time, the neutral stimulus can elicit a positive response without the desirable stimulus present.
Example of classical conditioning:
A user’s mobile device vibrates each time they order takeout from a food delivery app, eventually leading to an increase in orders.
- A user feels their mobile device vibrate after ordering.
- The user receives and consumes delicious food.
- The user makes many orders over the following weeks, each time feeling a vibration at checkout. Eventually, the user associates the vibration with the positive feelings related to the anticipation of eating.
- From then on, the user subconsciously thinks of ordering food whenever their mobile device vibrates. Orders increase.
2. Operant conditioning
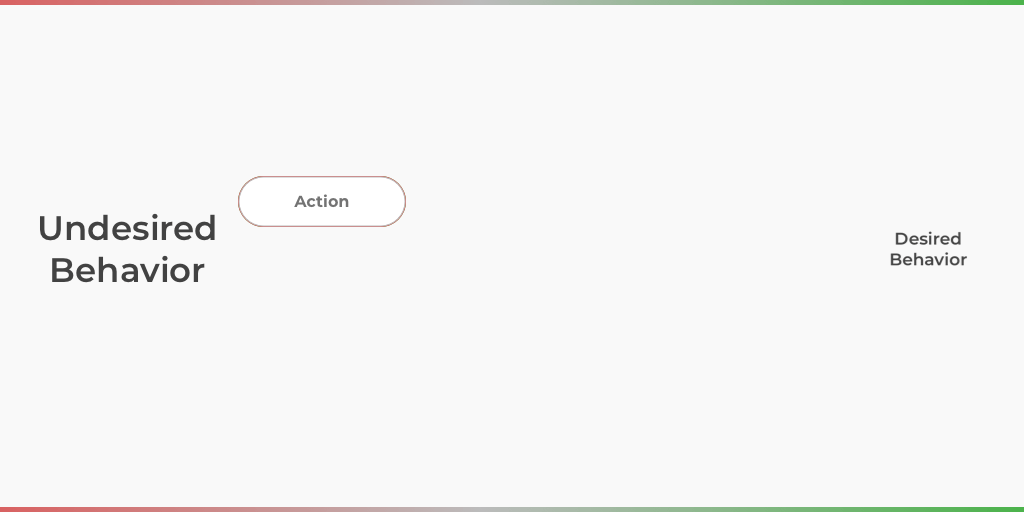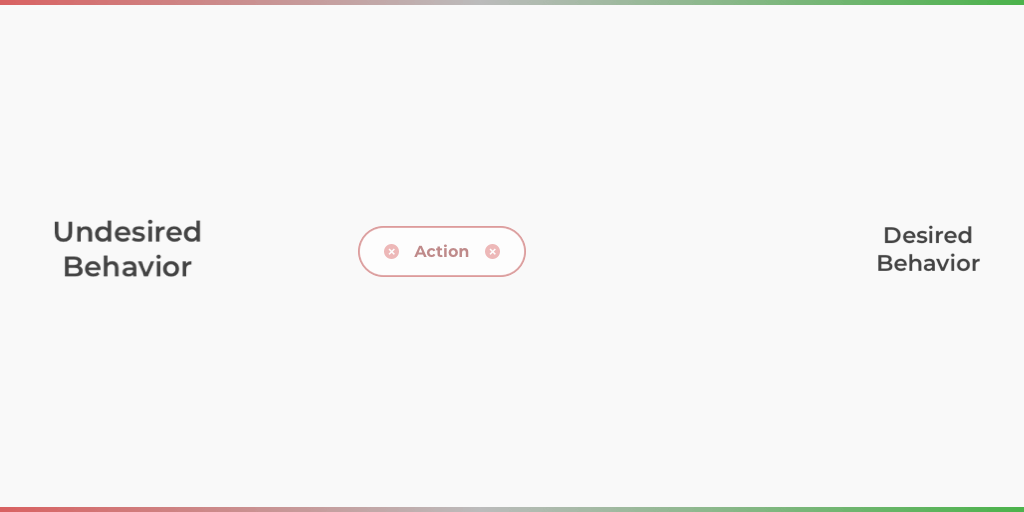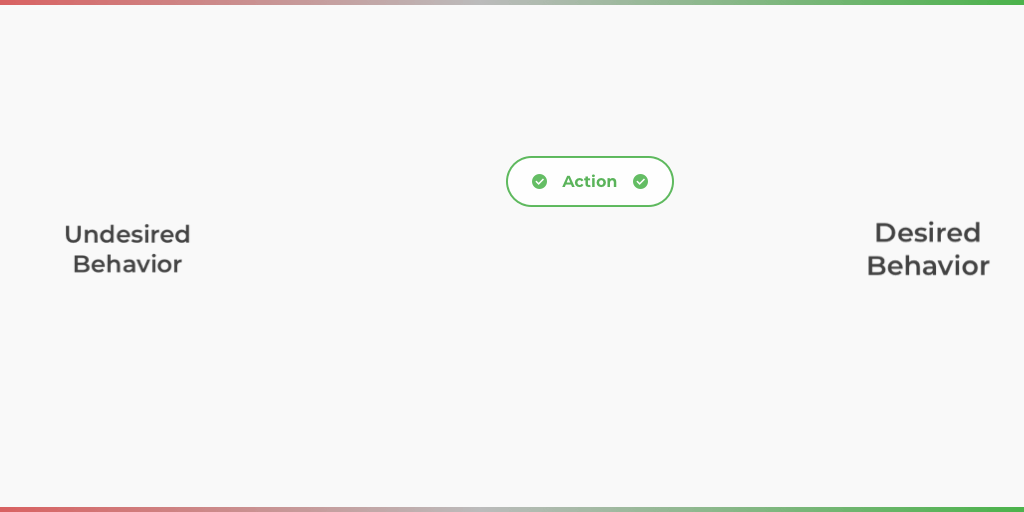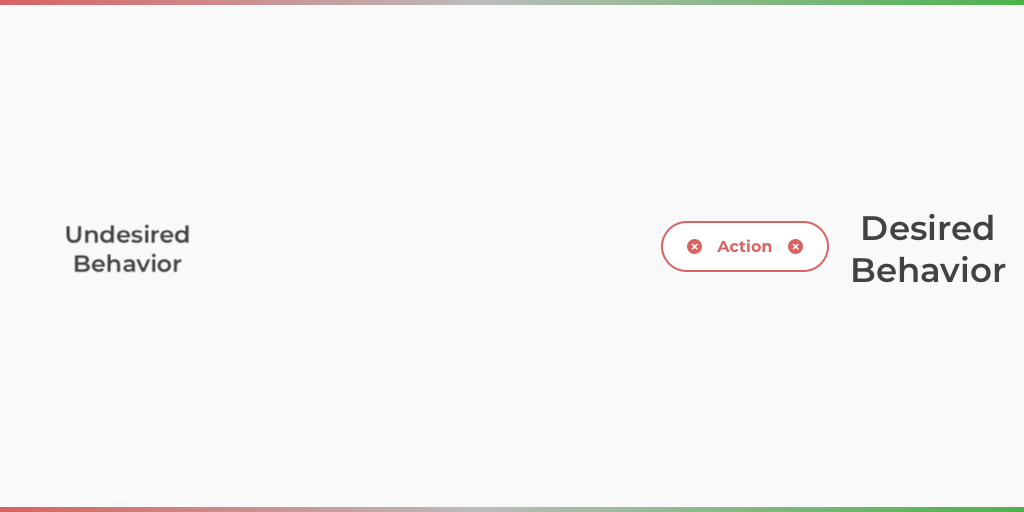
Operant conditioning is an associative learning process that guides an individual to desired behavior through the use of positive and negative reinforcement. Positive reinforcement is the addition of something that rewards or punishes an action. Negative reinforcement is the subtraction of something that rewards or punishes an action.
Example of operant conditioning:
A social media app wants users to post more content.
- The app makes the act of sharing easy and fun.
- Other users like the post and add comments.
- The likes and comments reinforce the act of posting content.
3. Shaping

Shaping is the reinforcement of different and successive approximations towards a targeted behavior. Employ a shaping strategy when a targeted behavior is complex or a difficult sell.
Example of shaping:
A VR editing app wants users to buy pre-built components.
- The app attracts users to view VR simulations built by others.
- The user can download assets from the simulations to build their own.
- As the user creates a simulation, they are presented with other components to use, both free and paid.
- The user decides to buy their first VR component.
Andrew Coyle
Andrew Coyle has worked as a designer for companies including Google, Intuit, and Flexport. He is currently the founder of NextUX, a visual editor and collaborative whiteboard.







