The game of Scrabble has changed little since its inception in the 1930s. There have been minor rule tweaks, but players today use basically the same rulebook and game board as players did 75 years ago. Much to game creator Alfred Mosher Butts’ credit, the distribution of letters and the point values for each letter have never changed. Continuity is certainly a notable attribute to Scrabble’s gameplay and success, but what the game really teaches UX practitioners—both in it’s design and in the way it’s played—is restraint.
Simplicity is sometimes mistaken for restraint, but restraint can only occur when there is the possibility of being complex or elaborate. Here, a choice is made to hold back and avoid complexity. Something that is merely simple may or may not offer the option to be complex. Butts had the opportunity to make Scrabble a complex game designed for only the best wordsmiths, but instead he held back and made the game widely accessible.
The game’s rules, its playing surface, the equipment, and the player’s strategy characterize restraint. It’s often tempting to play your best letters as soon as you get them, but the better strategy is to wait until you can use them most effectively to make a really great play. In this way, Scrabble, like the best websites and mobile applications, requires you—as player in the latter case and designer in the former—to exhibit restraint.
Designing with restraint means ensuring that the limits and boundaries of a website or application are clearly defined to the user. The best designs define those limits and boundaries without any explanation. As with Scrabble’s short rulebook and standardized game board, web designers must consider what the rules are for a website or application and maintain convention and standardization. The website DIY.org is an example of a site that is very complex, but has set boundaries and limitations.
The home page has just three options and there are clear and concise boundaries. The site’s rulebook is short and its navigation, succinct.
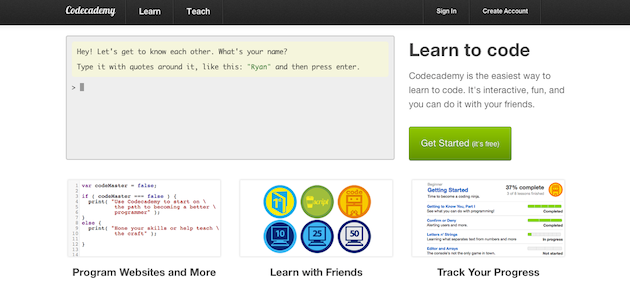
Codeacademy.com is another website that shows restraint. While it’s certainly possible to teach people how to code in a vast multitude of ways, Codeacademy has a standardized method built around quick, simple explanations. A site with as much information as Codeacademy provides could easily be flooded with intricate features and complex designs. Just like the design strategy behind Scrabble, however, the site is accessible to anyone, regardless of skill level, while simultaneously catering to people with advanced skills.
Graphic designers may want rich graphics and programmers may want to write broad, all-encompassing code, but way more often than not, the best experience for the user is a simple one. Part of the challenge of user experience design is to build systems using restraint. Rather than showing off, websites and applications often do better by holding back.
Keeping things simple and accessible certainly worked for Scrabble, which has been translated into about thirty languages and can be found in over half of the countries in the world. The game has sold millions of copies and there are dedicated players who take part in heated international tournaments.
(“Restraint” is, for our purposes, an ironically low-scoring word)
Scrabble could have been complex—it could have been crafted only for those with large vocabularies. Instead, Butts did something the best user experience practitioners do all the time: he designed a hugely accessible product using restraint.