Traditional Design thinking has laid the foundation for how problems are approached and addressed. It is still considered a valuable tool to address a problem. With the evolution of Generative AI, the focus has shifted towards integrating LLMs into workflows.
Across various sectors, from Agri-tech to Retail, there is a growing interest in developing conversational interfaces to promptly address inquiries. Whether the query is about attire for an event or determining the appropriate fertiliser for specific crops, LLMs are becoming increasingly relevant.
However, amidst this transition, the question arises, where should we begin? Herein lies the importance of an AI thinking process, which can serve as a guiding light.
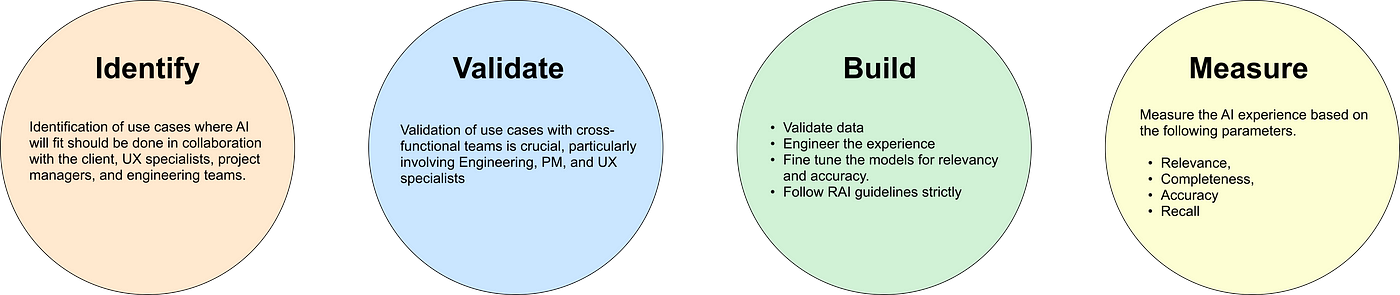
Here are the 4 stages of an AI thinking process explained in detail.
Identify
The first step is to identify use cases. Use cases typically originate from customers, and we need to make a careful consideration if the incorporation of AI can solve the core problem and further enhance the experience. In this step, we also need to figure out how we can leverage LLMs. LLMs can solve multiple problems ranging from language translation, text generation, and question answering to personalised recommendations, and many more. We must determine what specific tasks LLMs can solve and how they can be incorporated into the use case.
Validate
In this step, we need to figure out what is feasible to build. Can we deliver what the client expects? Do we have the required data to build an experience? Is the data good enough to consume? Is LLM capable of delivering what is expected? These questions can be best answered by conducting a POC (Proof of Concept), which is helpful as the experience can be shared with the client to obtain early feedback.
Build
In this step, we build the actual experience, and we fine tune the models to get relevant results. On the other hand, we adhere strictly to RAI (Responsible AI) guidelines. These guidelines ensure that the development process aligns with ethical principles and mitigates potential risks. By following RAI guidelines, we can create an experience that prioritizes transparency, fairness, accountability, and privacy while harnessing the power of AI technology.
Measure
Measuring AI experiences can be based on parameters such as relevance, completeness, accuracy, and recall [1]. This step is considered the most important in the AI thinking process, where the objective is to verify whether the experience can deliver the expected results. There are several popular benchmarks such as GLUE (General Language Understanding Evaluation), BLEU, and ROUGE. We can use these popular metrics or derive one relevant to your use cases.
Reference: [1 ]Debarag Banerjee, Pooja Singh, Arjun Avadhanam, Saksham Srivastava Benchmarking LLM powered Chatbots: Methods and Metrics (2023).