Save

In many rural communities around the world, a lack of access to financial resources creates a significant obstacle to progress. Residents often rely on traditional methods of managing their money, such as keeping cash at home. While these practices offer a sense of control, they make it difficult to build a credit history or access loans from conventional banks. This lack of a credit profile can be a major hurdle, as traditional lenders depend heavily on credit scores to assess risk¹.
Consider Linda, a small-scale farmer in Southeast Asia. Like many others in her community, Linda dreams of growing her farm. However, the idea of saving beyond keeping cash at home feels like an insurmountable obstacle. Limited access to banks, or even the perception of limited access, discourages her. Even if a bank were readily available, hidden fees and minimum balance requirements can feel like a burden on her limited income. Past experiences or a general distrust of the banking system further complicate things. For Linda, the perceived control over her cash outweighs the benefits of formal banking, which can sometimes feel intrusive with its regulations.
Furthermore, this reliance on cash leaves Linda vulnerable in times of crisis. Imagine a family emergency or a crop failure. Without a formal account, Linda lacks the safety net of a formal financial system and is forced to turn to informal lenders with predatory lending practices. This not only traps her in a cycle of debt but also hinders her ability to build long-term financial security. Keeping cash at home also offers minimal returns, preventing her from growing her assets and accumulating an emergency fund.
This issue is widespread — only 27% in Southeast Asia have bank accounts, leaving millions unbanked.
Countries with developing financial infrastructure, like Cambodia, see even lower rates (See our Inclusive report here). Linda’s story isn’t unique. Millions face similar challenges, highlighting the urgent need for more inclusive financial systems.
While Linda might not meet traditional credit score criteria, alternative assessments based on her specific situation could be used. Examining both income and payment records can offer a clearer view of her financial trustworthiness².
If we imagine a future where this kind of information can be easily collected, how could AI help bridge the gap for people like Linda?
The Power of Groups, Enhanced by AI
In rural communities around the world, a powerful force exists: close-knit social networks. People readily support each other, reflecting a spirit of mutual aid. In Indonesia, this concept is called “gotong royong.” This strong sense of community is a key ingredient in the success of the Grameen Bank model, founded by Nobel laureate Muhammad Yunus in Bangladesh.
The Grameen Bank specifically targets individuals who lack traditional collateral for loans, often women living in poverty. Their innovative approach revolves around microloans — small loans starting at just USD25 — provided to groups, not individuals.
This fosters a strong sense of shared responsibility and community support. Each group member is accountable for repaying their portion of the loan, creating a powerful incentive for everyone to succeed. Imagine it as a team effort — if one member falls behind, it impacts the entire group’s ability to access future loans. To ensure accountability, loan officers from the Grameen Bank typically visit communities weekly. The loan amounts are kept small to prevent overextension, and repayments are structured as frequent, manageable installments. This frequent interaction also allows the bank to identify and address any issues within the groups early on.
How can we leverage technology to build upon this successful model and further empower individuals like Linda in similar situations around the world?
We explored the AI’s power that lies in analyzing alternative data sources. By considering things like consistent e-commerce cash-on-delivery payments or contributions to local savings groups, AI can create more comprehensive credit profiles for individuals like Linda, even without a formal banking history. This empowers lenders to assess creditworthiness beyond traditional models, ultimately helping more people build financial security.
Here’s how the Grameen Bank model works:
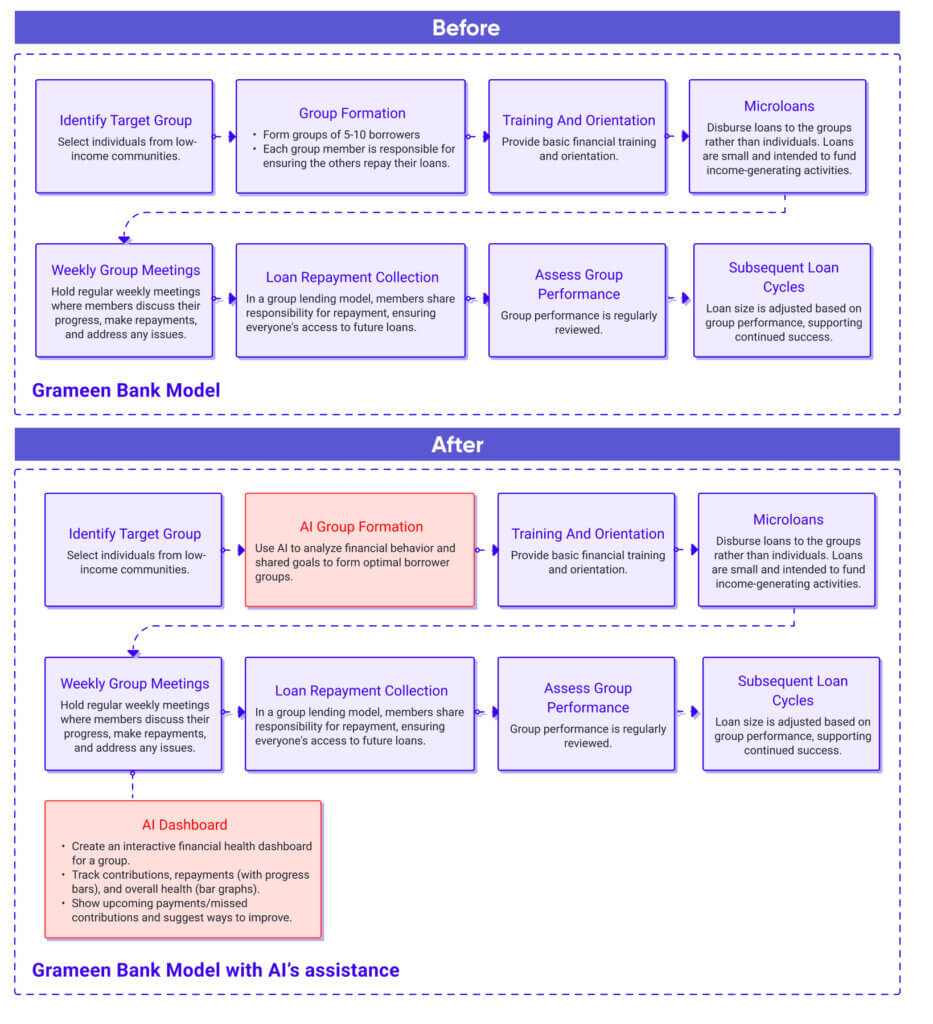
Here’s how AI can specifically amplify the power of groups:
Automated Group Formation and Management
AI can replicate the group lending model by automating group formation. It can consider factors like financial behavior based on digital footprints, and shared goals to create well-matched groups with a high likelihood of success. AI can also automate group management tasks like tracking contributions and monitoring repayment behaviors, freeing up resources for human interaction and support.
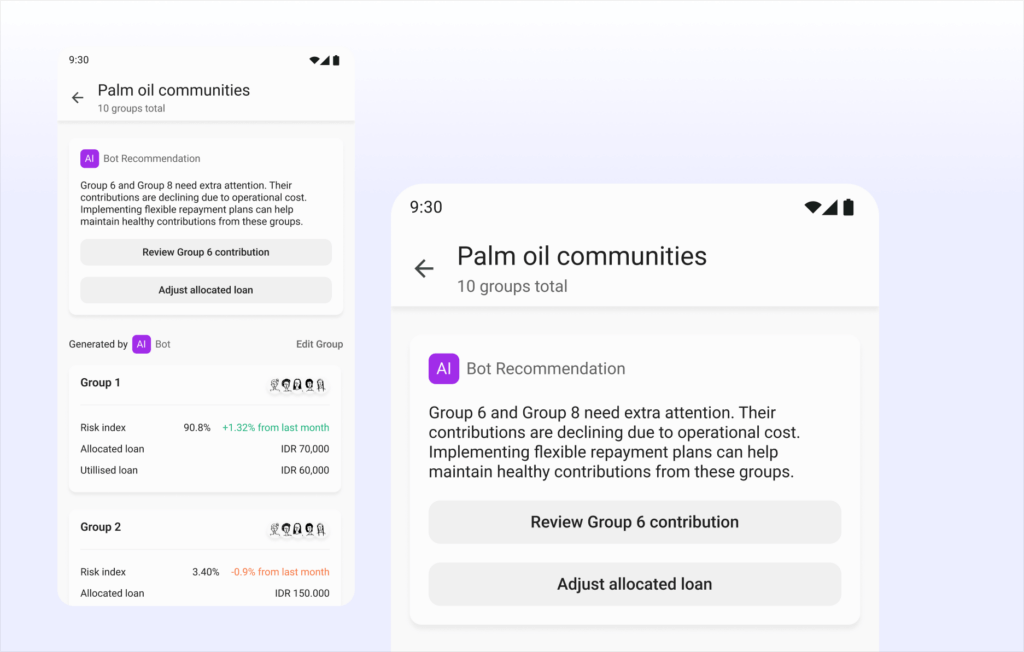
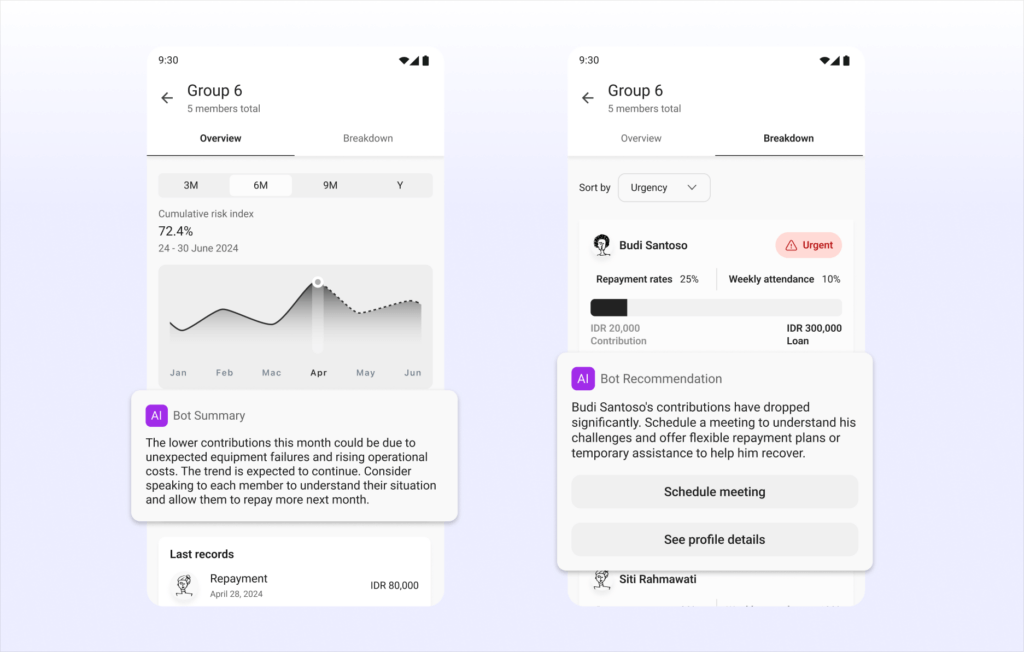
Real-Time Insights and Support
AI can analyze group dynamics and identify potential issues early on. It can provide targeted interventions or suggest support mechanisms to struggling groups before defaults occur. Additionally, AI can personalize loan terms based on the group’s overall risk profile, ensuring fair and sustainable lending practices.
Conclusion
For generations, rural communities have thrived on “gotong royong,” a spirit of mutual support that has helped them weather challenges. The success of the Grameen Bank further underscores the power of strong communities in achieving financial inclusion. However, even the most time-tested traditions can benefit from a modern boost.
This is where Artificial Intelligence (AI) steps in. With its rise, we have a unique opportunity, not to replace “gotong royong,” but to make it even stronger. Imagine AI tools that analyze data from financial institutions and fintech companies, identifying creditworthy individuals who might not qualify under traditional systems. These AI insights can then seamlessly connect with existing social networks, empowering “gotong royong” groups to extend their reach and effectiveness. This would foster a more secure, transparent, and inclusive financial system within these communities.
Of course, such a vision requires careful planning and collaboration. The data used by AI needs to be reliable and reflect the specific situations of these communities. Additionally, we must determine the appropriate weight given to AI analysis within the decision-making process.
While the AI infrastructure for this purpose is still under development, fueled by data shared by financial institutions and fintech companies, the potential benefits are undeniable. As this infrastructure matures, it holds the promise of equipping rural communities with the tools they need to thrive — a powerful combination of tradition and technology that can bring greater economic stability and prosperity.
¹Bank, Asian Development. “Enhancing Small Enterprises’ Access to Finance: ADB’s Take.”, 1 Aug. 2014, https://www.adb.org/features/enhancing-small-enterprises-access-finance-adbs-take Accessed 17 July 2024.
²“Guide to Alternative Credit Scoring.” SEON, seon.io/resources/guides/alternative-credit-scoring/
The article originally appeared on Medium.
Thasya Ingriany
Thasya is a Creative Strategist at Sixty Two who excels in identifying growth opportunities and crafting narratives that resonate effectively with the Sixty Two audience, aligning these strategies seamlessly with Project Lima's overarching goals. Read more of her works on Medium.
- The article explores how AI can enhance financial systems for the unbanked by using alternative data to create accessible, user-friendly credit profiles for rural entrepreneurs.
- It analyzes how AI can automate group lending practices, improve financial inclusion, and support rural entrepreneurs by strengthening community-driven financial networks like “gotong royong”.